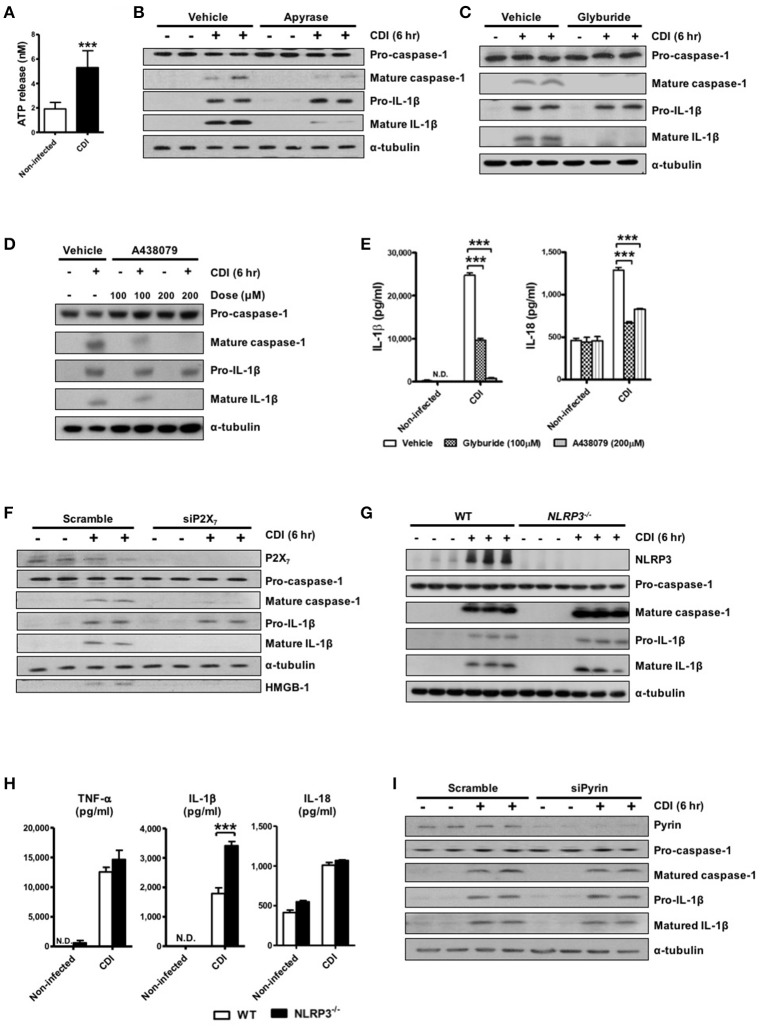
Figure 2.
ATP-P2X7 pathway is essential for C. difficile-induced inflammasome activation. (A) ATP quantification in peritoneal macrophage supernatant after C. difficile VPI 10463 infection. (B–D) Peritoneal macrophages were infected with C. difficile VPI 10463 in the presence of apyrase (5 units/ml), glyburide (100 μM) or a 30-min pretreatment with the P2X7 antagonist (A438079) for 6 h. ***p < 0.001. Inflammasome activation, including IL-1β and caspase-1 processing, was analyzed by Western blotting. (E) The levels of IL-1β and IL-18 in the supernatant of infected cells after inhibitor treatment were determined by ELISA. ***p < 0.001, compared with vehicle-treated infected group. (F) Western blot analysis of inflammasome activation after transfection with scrambled siRNA or P2X7 siRNA in infected THP-1 cells. (G) IL-1β production and caspase-1 activation between WT and NLRP3−/− infected cells were detected by Western blotting. (H) The secretion of IL-1β, IL-18, and TNF-α were monitored by ELISA. Values represent the mean ± SEM (N = 3/group). ***p < 0.001. N.D., not detected. (I) Western blot analysis of inflammasome activation after transfection with scrambled siRNA or Pyrin siRNA in infected THP-1 cells.