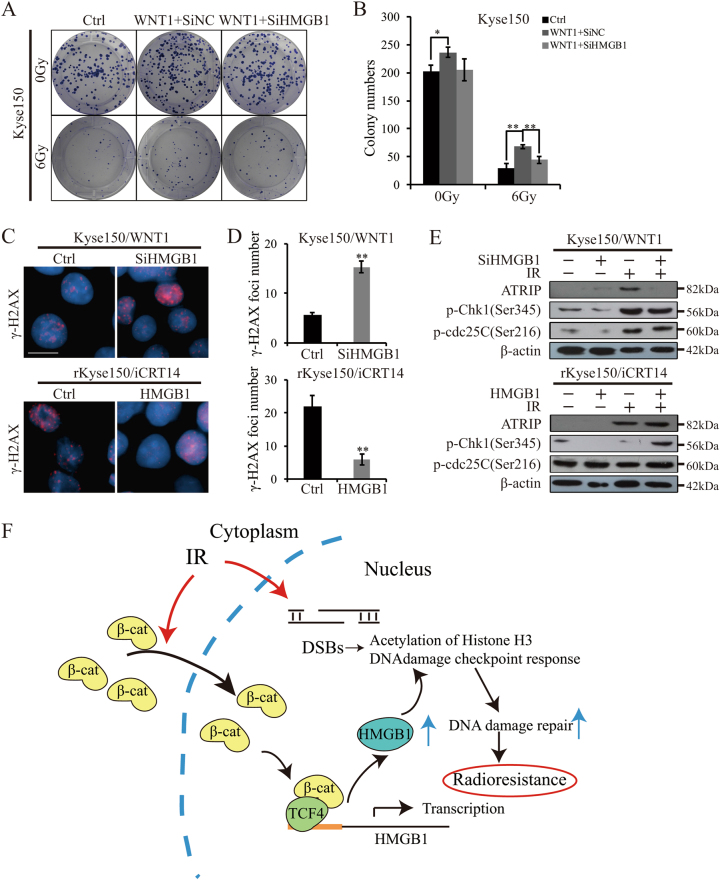
Fig. 7 HMGB1 partly mediated Wnt-induced radioresistance.
a Survival clonogenic assay. Kyse150 cells stably transfected with plenti/SiHMGB1 (NC as control) treated with WNT1 were collected to perform clonogenic assays with or without IR. b Quantification of colony numbers from a. Mean ± SD, N = 3, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. c IF staining of phosphor-γH2AX. 24 h after WNT1 treatment for Kyse150/SiHMGB1 and Kyse150/SiNC cells and 24 h after iCRT14 treatment for rKyse150/HMGB1 and rKyse150/NC cells, cells were exposed to IR. 24 h after IR, IF staining of phosphor-γH2AX were performed to assess the DNA damage levels. Scale bars = 20 μm. d Mean numbers of γH2AX foci. Mean ± SD, N = 3, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. The results were from c. e Western blotting analysis of representative proteins of DNA damage checkpoint response. The expression levels of ATRIP, p-cdc25C, and p-Chk1in Kyse150/SiHMGB1 (Kyse150/SiNC) cells with WNT1 treatment and rKyse150/HMGB1 (rKyse150/NC) cells with iCRT14 treatment were assessed via western blotting. f Schematic diagram. Upon IR exposure, β-catenin enters the nucleus and binds with TCF4, thus transactivating HMGB1. HMGB1 then acting as the chromatin modifier, promotes the acetylation of histones H3 and the activation of DNA damage response, which induces cellular radioresistance