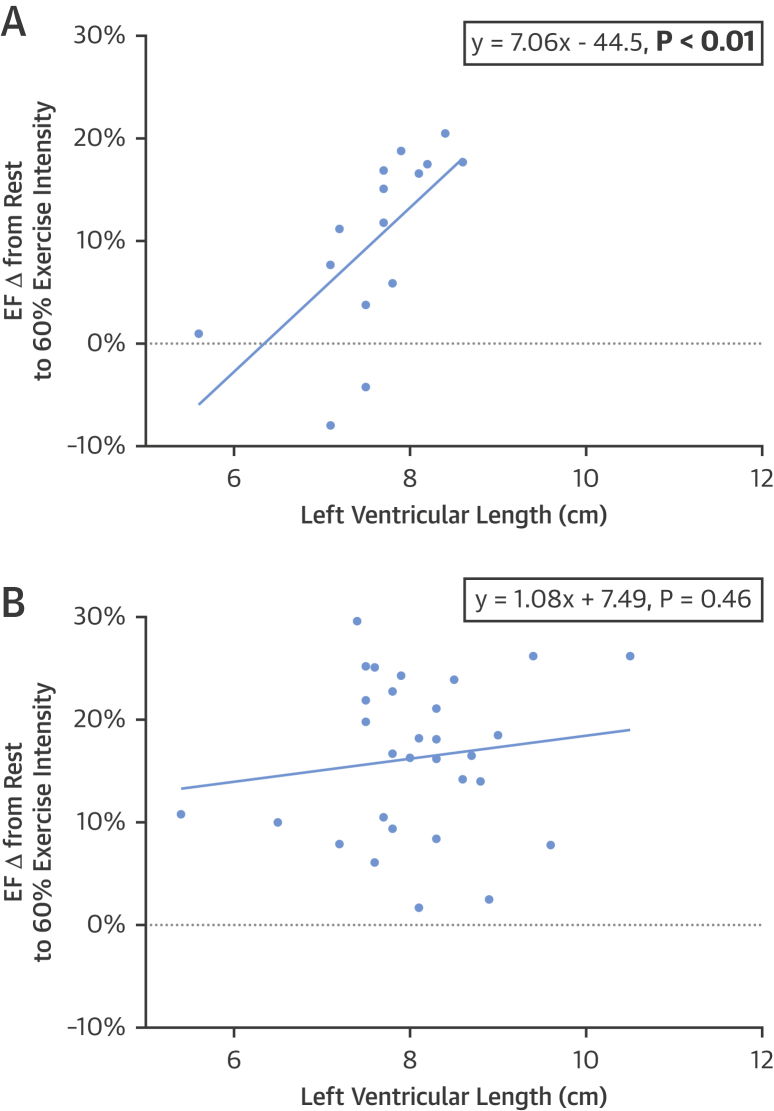
Figure 2.
Relationship Between Left Ventricular Length and Change in Ejection Fraction When Going From Rest to 60% Exercise Intensity in Preterm-Born Versus Term-Born Young Adults
(A) In preterm-born adults, greater left ventricular (LV) length was strongly correlated with increasing ejection fraction (EF) when going from rest to 60% exercise intensity (p < 0.01). (B) In term-born adults, LV length was not correlated with a change in EF when going from rest to 60% exercise intensity (p = 0.46).