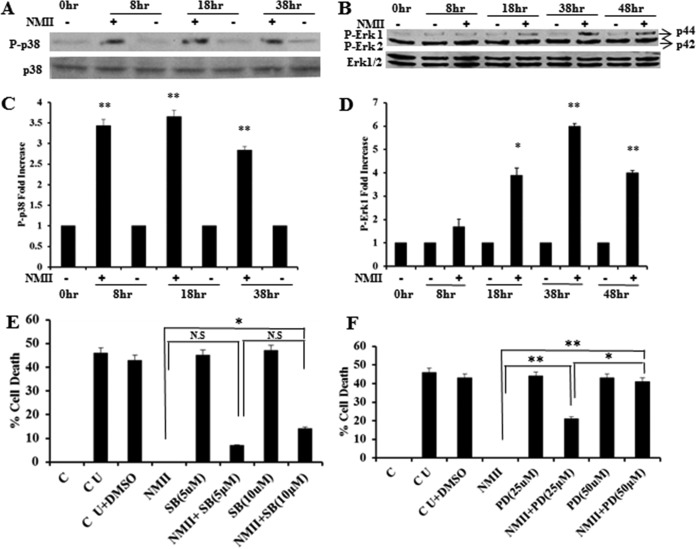
FIG 4.
NMII activates MAPK p38 and Erk1 for inhibition of neutrophil apoptosis. (A) Analysis of phosphorylated p38 in BMNs infected with NMII at an MOI of 100 by Western blotting at 8, 18, and 38 hpi. (B) Analysis of phosphorylated Erk1/2 in BMNs infected with NMII at an MOI of 100 by Western blotting at 8, 18, 38, and 48 hpi. (C) Fold increase in the number of intensity units of the phosphorylated p38 protein band. (D) Fold increase in the number of intensity units of the phosphorylated Erk1 protein band. (E) BMNs were untreated or treated with 5 or 10 μM the p38 inhibitor SB203580 for 1 h prior to infection with NMII at an MOI of 100. The percent cell death of BMNs with different treatments was measured by the MTS assay at 18 hpi. (F) BMNs were untreated or treated with 25 or 50 μM the Erk1/2 inhibitor PD98059 for 1 h prior to infection with NMII at an MOI of 100. The percent cell death of BMNs receiving different treatments was measured by the MTS assay at 18 hpi. Error bars represent the standard deviation from the mean. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; N.S, not significant. P-p38, phosphorylated p38; P-Erk1 and P-Erk2, phosphorylated Erk1 and Erk2, respectively; SB, SB203580; PD, PD98059; C, 0-h time point, fresh uninfected BMNs; CU, uninfected control BMNs incubated for the indicated times; CU+DMSO, inhibitor buffer (dimethyl sulfoxide [DMSO])-treated uninfected BMNs.