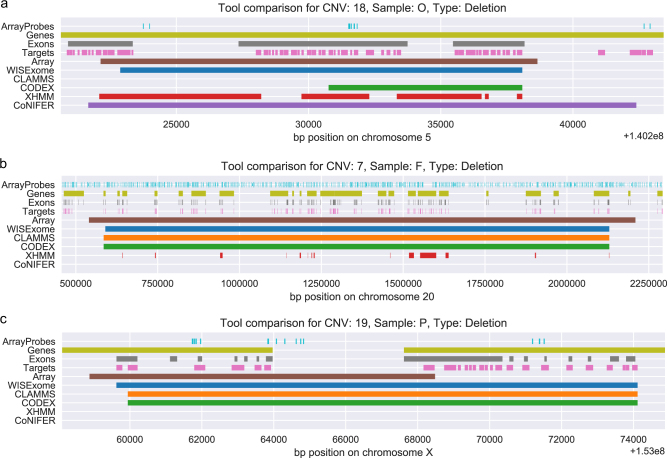
Fig. 2.
Detected CNV segments by WISExome (blue), CLAMMS (orange), CODEX (green), XHMM (red), and CoNIFER (purple) for three known pathogenic CNVs according to the array analysis (brown). The region is annotated by the array probes (cyan), genes (citron), exons (gray), and target regions (pink). CNVs shown here are marked in Supplementary Table S1 as numbers 18 (a), 7 (b), and 19 (c). a CLAMMS failed to identify this region as aberrated. WISExome, XHMM, and CoNIFER mark roughly the same area as part of a CNV, while CODEX made a relatively small call. b WISExome, CLAMMS, and CODEX are in near-perfect agreement on the CNV. XHMM shows a very fragmented call, failing to identify several affected genes in between its calls. CoNIFER does not make a call. c WISExome, CLAMMS, and CODEX all identify the region to the right as aberrated, while the CNV should have been shorter according to the array. Both XHMM and CoNIFER fail to make a call.