Figure 3.
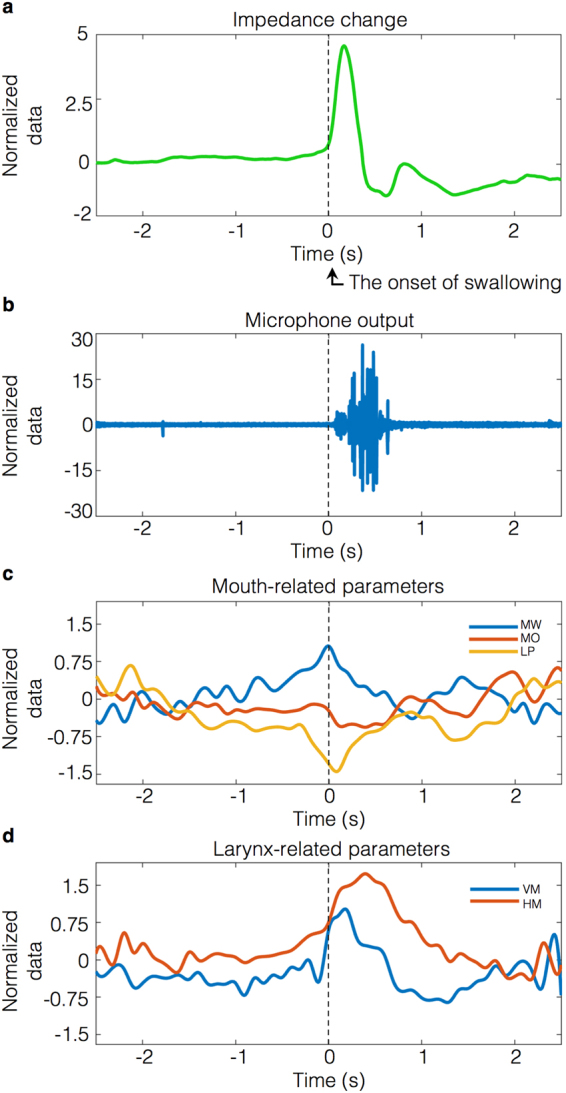
Representative waveforms of Participant 1. These waveforms were traced from a 30-year-old male participant (Participant 1) and were calculated by the additional averaging of signals that were time-locked to the onset of swallowing. (a) Signals recorded by the laryngograph (EGG) changed upon swallowing. The onset of swallowing was detected at the initial rise of the waveform. (b) The waveforms were recorded by a throat microphone. The sounds of swallowing were caused by a food bolus passing through the pharynx. (c) The mouth-related parameters MW, MO, and LP changed during swallowing. These parameters began to change before swallowing and exhibited positive or negative peaks at the onset of swallowing. (d) The larynx-related parameters VM (vertical motion) and HM (horizontal motion) did not exhibit appreciable changes before swallowing, but these parameters suddenly exhibited a positive peak immediately after swallowing.
