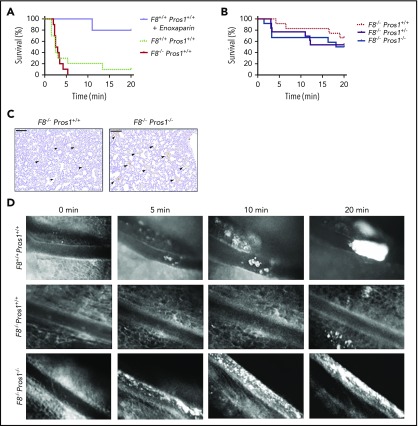
Figure 2.
Murine models of thrombosis. (A-C) TF-induced venous thromboembolism in F8+/+ Pros1+/+, F8−/− Pros1+/+, F8−/− Pros1+/−, and F8−/− Pros1−/− mice (n = 10 per genotype). Anesthetized mice were injected intravenously via the inferior vena cava with different doses of recombinant TF (Innovin): 1/2 dilution (∼4.3 nM TF) in panel A and 1/4 dilution (∼2.1 nM TF) in panels B-C. In panel A, one group of F8+/+Pros1+/+ mice received an injection of the low molecular weight heparin (enoxaparin 60 µg/g s.c.). The time to onset of respiratory arrest that lasted at least 2 minutes was recorded. Experiments were terminated at 20 minutes. Kaplan-Meier survival curves (A-B). (C) Two minutes after onset of respiratory arrest or at the completion of the 20-minute observation period, lungs were excised and investigated for fibrin clots (indicated by arrowheads, immunostaining for insoluble fibrin, monoclonal antibody clone 102-10) Scale bars: 200 μm. (D) Thrombus formation in FeCl3-injured mesenteric arteries recorded by intravital microscopy in F8+/+ Pros1+/+, F8−/− Pros1+/+, and F8−/− Pros1−/− mice, representative experiment (n = 3 per genotype).