Figure 7.
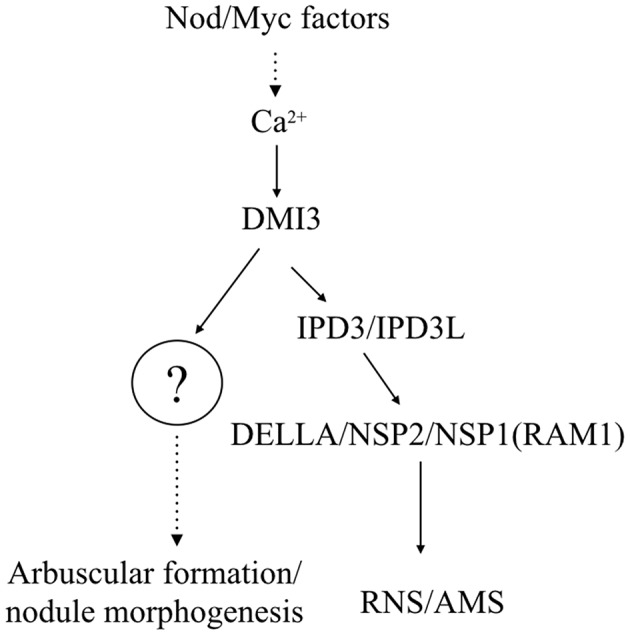
Working model of IPD3s transcription factors in rhizobial and mycorrhizal symbioses. These signaling pathways are an amalgamation of genetic analyses in Lotus japonicus and Medicago truncatula; gene names are indicated for M. truncatula. Calcium- and calmodulin-dependent protein kinase (CCaMK/DMI3) is responsible for decoding the calcium spiking and phosphorylates IPD3. In this model, the phosphorylation level of IPD3 controls the ability of IPD3 to bind the ERN1 promoter. Interestingly, an unknown protein or other phosphralation sites of IPD3 may help to retain the stability of the IPD3 complex, or may act in parallel with IPD3 through binding DELLAs to activate downstream gene expression to initiate arbuscular formation and nodule morphogenesis.
