Fig. 2.
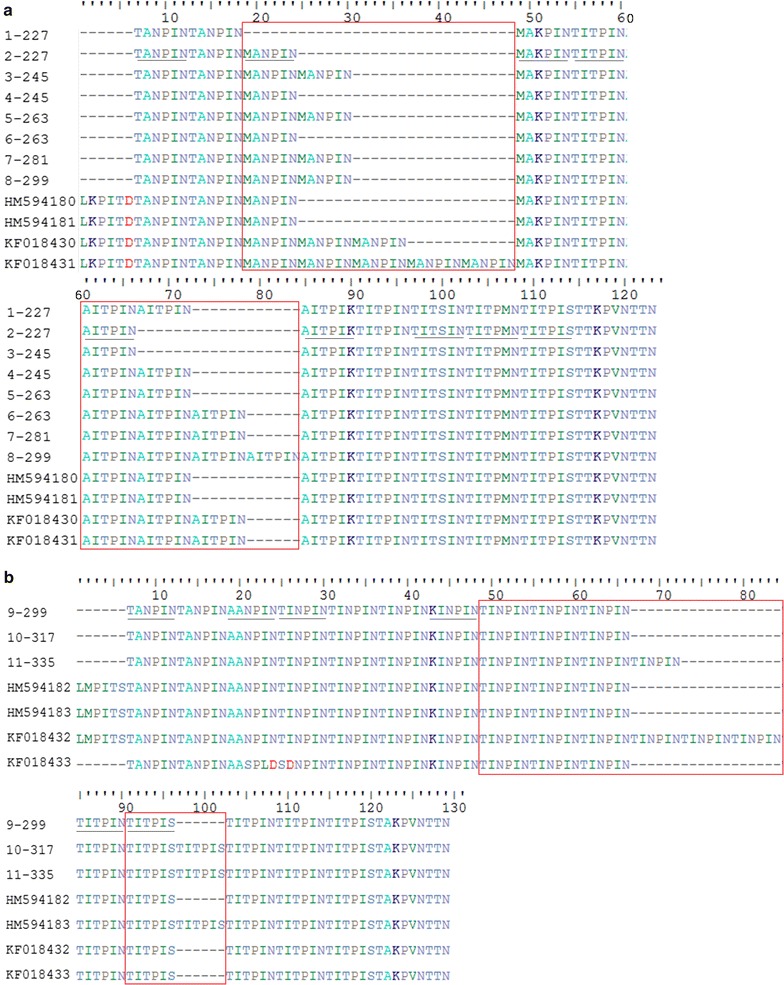
Amino acid sequence alignment of the distinct potra fragments amplified from 11 genotypes of Plasmodium ovale and the reference sequences. a P. ovale wallikeri; b P. ovale curtisi. Six amino acids were one amino acid unit which were underlined. P. o. wallikeri was mainly composed with nine kinds of amino acid units, TANPIN, MANPIN, MAKPIN, TITPIN, AITPIN, AITPIK, TITSIN, TITPMN and TITPIS. While P. o. curtisi had six kinds of amino acid units, TANPIN, AANPIN, TINPIN, KINPIN, TITPIN and TITPIS. Boxed sequences represented the dominant amino acid repeats that differed in the number of amino acid units. The sequences of P. o. wallikeri were characterized by two amino acid units, MANPIN and AITPIN. The sequences of P. o. curtisi were characterized by amino acid units TINPIN and TITPIS
