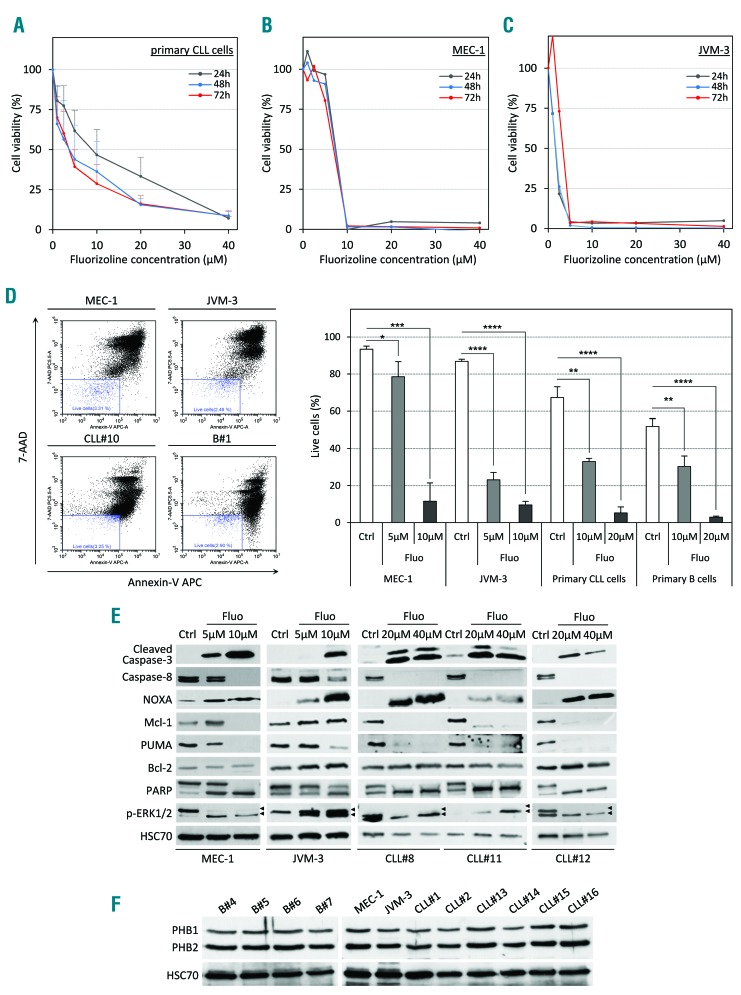
Figure 1.
Fluorizoline (fluo) efficiently induces apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells in vitro. (A–C) Cytotoxic dose response of fluo on primary human CLL cells (A), CLL cell lines MEC-1 (B) and JVM-3 (C) was analyzed by CCK8 assay. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from 7 CLL patients as well as the CLL cell lines MEC-1 and JVM-3 were treated with increasing doses of fluo ranging from 1 μM to 40 μM for 24 hours (h) (gray line), 48 h (blue line) or 72 h (red line). (D) Representative scatter plots illustrating annexin-V/7-AAD staining of cells after 24 h of treatment (left panel). MEC-1 (upper left plot), JVM-3 (upper right plot), primary CLL cells (lower left plot, patients CLL#8 to CLL#10), and normal B cells (lower right plot, donors B#1 to B#3) were treated with 5–20 μM fluo or with equivalent volume of the vehicle dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) for 24 h and stained with annexin V-APC and 7-AAD prior to analysis by flow cytometry. Viable cells (annexin V-APC negative/7-AAD negative, blue gate) were determined and are expressed as percentage of total cell population. Data represent average percentage of live cells (right panel) from independent experiments (n=3). *P<0.05, **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P<0.0001. (E) MEC-1, JVM-3 and primary CLL cells (patients CLL#8, CLL#11 and CLL#12) were treated with 5 μM to 40 μM fluorizoline or with equivalent volume of the vehicle DMSO (Ctrl) for 24 h, lysed and proteins were analyzed by western blot with the indicated antibodies. HSC70 protein served as a loading control. (F) The expression of PHB1 and PHB2 was analyzed by western blot in total cell lysates from normal B cells (donors B#4 to B#7), MEC-1 and JVM-3 cells, and primary CLL B cells (patients CLL#1, CLL#2 and CLL#13 to CLL#16). HSC70 protein served as a loading control.