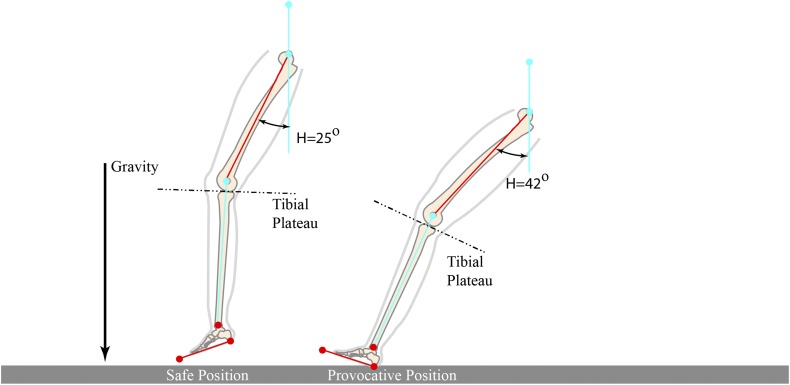
Fig. 6.
Illustrations showing the variation in tibial slope at low hip-flexion angles (safe position) and high hip-flexion angles (provocative position) relative to the gravitational vector. The average hip angles were obtained from the study by Sheehan et al.16. The average ankle and knee angles were obtained from the study by Boden et al.17. It should be noted that the inherent slope of the tibial plateau for both images was assumed to be 6°. (Reprinted, with modification, from: Boden BP, Breit I, Sheehan FT. Tibiofemoral alignment: contributing factors to noncontact anterior cruciate ligament injury. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009 Oct;91[10]:2381-9.)