Figure 4. Facilitation mediated by syt7.
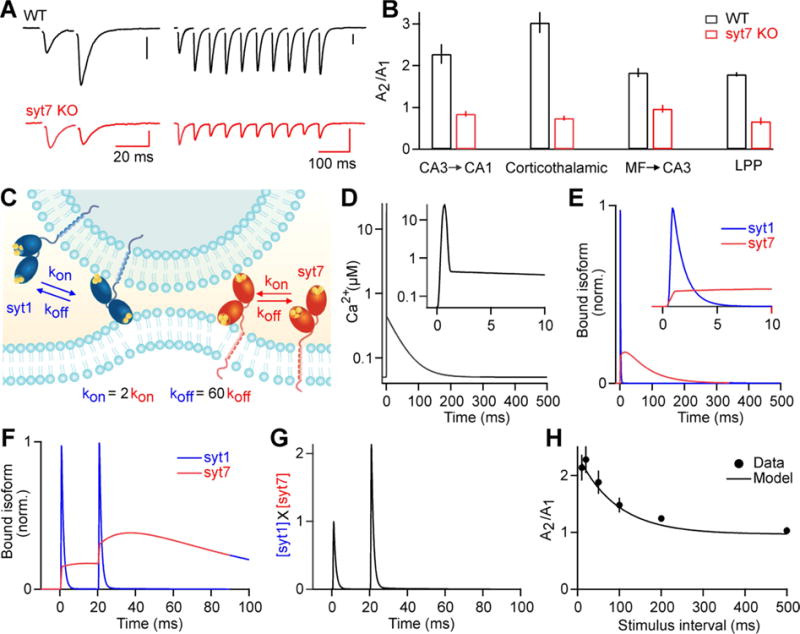
A) EPSCs recorded from CA1 pyramidal cells in WT and syt7 KO mice. Vertical scale bars 100 pA. Adapted from Jackman et al. (2016).
B) Paired-pulse ratios at 20 ms intervals, from hippocampal Schaffer collaterals (CA3 ➔ CA1), corticothalamic synapses, hippocampal mossy fibers (MF ➔ CA3), and hippocampal lateral perforant path synapses (LPP) from WT and syt7 KO mice.
C) In the presence of Ca2+, the C2A domain of syt1 binds to phospholipids twice as fast as the C2A domain syt7, and unbinds ~60-fold faster than syt7 (Brandt et al., 2012).
D) Simulated Ca2+ signal at a release site following an action potential. During the action potential, local Ca2+ rises to 25 μM briefly (FWHM = .34 ms, Sabatini and Regehr, 1998)). After the action potential, a residual Ca2+ signal of 400 nM decays back to resting Ca2+ (50 nM) with a 40 ms time constant (Brenowitz and Regehr, 2007).
E) Simulated phospholipid binding of both syt1 and syt7 during a single action potential, normalized to the maximal binding produced by a train of 10 action potentials at 100 Hz.
F) Phospholipid binding in response to a pair of action potentials.
G) The multiplied fraction of bound syt1 and bound syt7 ([syt1]X[syt7]), normalized to the peak initial response.
H) Paired-pulse ratios at different stimulus intervals recorded from Schaffer collateral synapses (adapted from Jackman et al. (2016)), along with the facilitation predicted by [syt1]X[syt7].
(E-H) Phospholipid binding was simulated using parameters from stopped-flow experiments of syt association with PIP2-containing target membrane liposomes (Brandt et al., 2012). Kd for Ca2+ was 41 μM and 1.5 μM, with a cooperativity of 1.9 and 2.8 for syt1 and syt7 respectively. For comparison to physiological recordings, binding kinetics were adjusted for temperature (34° C) (Hui et al., 2005). Koff 900 s−1 and 15 s−1 and Kon 415 s−1 and 190 s−1, for syt1 and syt7 respectively.
