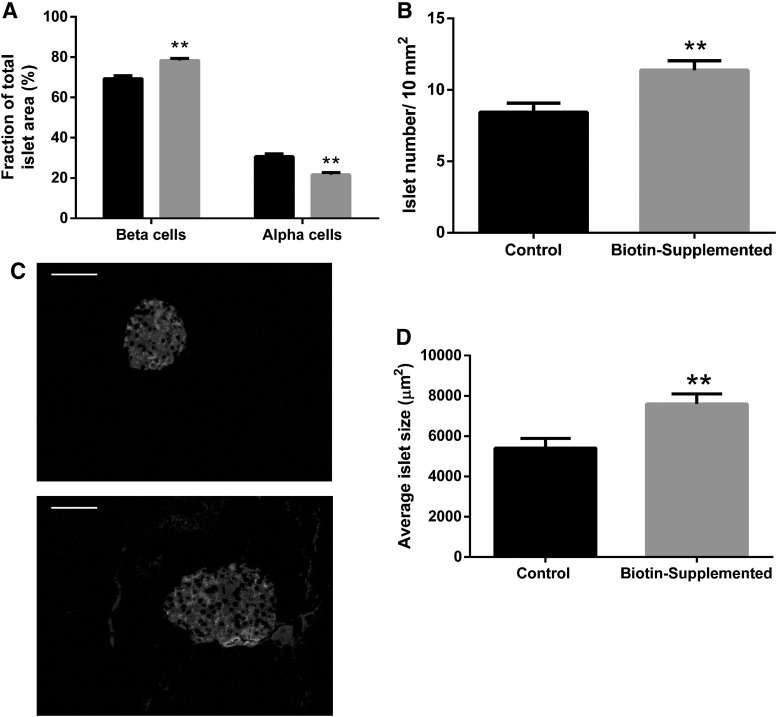
FIG. 2.
Effect of biotin supplementation on islet morphometry and morphology. Morphometry from pancreatic sections of control and biotin-supplemented mice. (A) Mean proportions of alpha- and beta-area for islet area. Significance was assessed by Mann–Whitney U test. **P ≤ .005 compared with the control group. (B) Islet number per pancreatic area (10 mm2). Significance was assessed by Student's t-test. **P ≤ .005 compared with the control group. (C) Immunofluorescence images of pancreatic islets from control (C, upper panel) and biotin-supplemented (C, bottom panel) mice pancreas sections stained for insulin and glucagon. Scale bar represents 50 μm. (D) Average islet size (μm2) ± SEM. Significance was assessed by Mann–Whitney U test. Values are mean ± SEM. n = 4 mice per group. **P ≤ .005 compared with the control group.