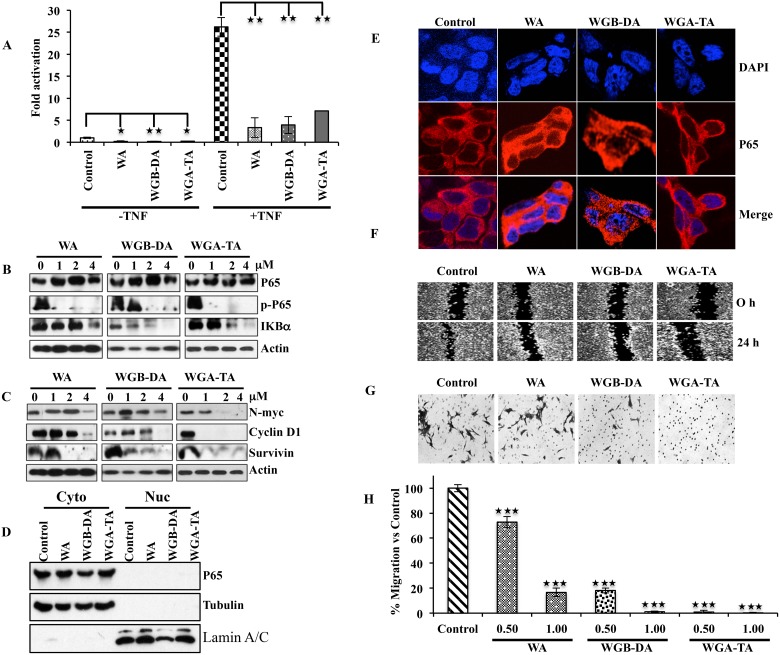
Figure 6. Down regulation of the NF-κB activity after withanolide treatment leads to down regulation of p-p65 (ser536), targets N-myc and prevents migration as well as invasion of NB cells.
(A) NB cell line IMR 32 was transfected with 0.5 mg of NF-kB reporter along with 50 ng of renilla luciferase by lipofectamine 2000. 24 h post transfection, the cells either were treated with 2 μM withanolides (WA, WGB-DA or WGA-TA) for 3 h before treatment with TNF-α for 16 h for TNF-α mediated NF-κB activity and left untreated for uninduced NF-κB activity. The luciferase activity was measured 24 h post addition of withanolides using Promega dual luciferase assay kit. (B) Western blot analysis of p-p65 (ser536) and Iκ-Bα demonstrating degradation of Iκ-Bα and down regulation of phospho-p65 (ser 536) whereas total levels of p65 remains unchanged. (C) Down regulation of NF-κB target genes such as N-myc, cyclin D1 and survivin in a dose dependent manner after 24 h treatment of IMR 32 cells with withanolides. (D and E). Imuuno fluorescence analysis of p65 after withanolides treatment evaluated by confocal microscopy indicated cytosolic presence of p65. Absence of nuclear staining of p65 showed inhibition of NF-κB due to prevention of nuclear localization of p65. DAPI was used for staining nuclei. This was further confirmed by the cytosolic and nuclear fractionation immunoblots. The same blot was stripped and reprobed for tubulin and lamin A/C after immunoblotting for p65 to verify the integrity of the cytosolic and nuclear fractions. (F–H). The acetate derivatives effectively block migration and invasion of IMR 32 cells as seen in wound healing and Boyden chamber invasion assays.