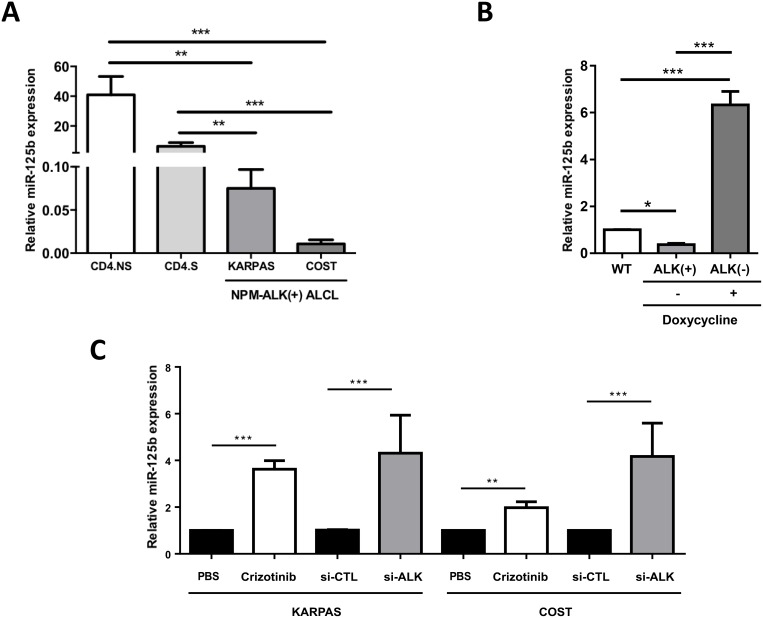
Figure 1. NPM-ALK represses the expression of miR-125b in ALCL human and mouse models.
(A) Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis of miR-125b expression in two NPM-ALK(+) ALCL cell lines (KARPAS-299 and COST) and CD4 lymphocytes stimulated (S) or not (NS) with CD3/CD28 antibodies. SNORD44 expression was used as an internal control. Relative human miR-125b expression was expressed as 2–ΔCt relative to SNORD44 expression. (B) Assessment of miR-125b expression by qRT-PCR in wild type mice (WT, N = 6) or NPM-ALK transgenic mice containing a Tet-OFF system treated (+) or not (−) with doxycycline (N = 6; B). SNORD202 expression served as the internal control, and the relative ratio of mmu-miR-125b expression was expressed as 2–ΔΔCt relative to WT mice. (C) MiR-125b expression in KARPAS-299 and COST cells treated for 72 hours or not (PBS) with crizotinib or transfected with either an irrelevant siRNA as the negative control (si-CTL) or a siRNA targeting ALK mRNA (si-ALK). SNORD44 expression served as the internal control and the relative ratio of hsa-miR-125b expression was expressed as 2–ΔΔCt relative to untreated cells or to the si-CTL conditions. Data represent means ± SEM (bars) from 3 independent experiments. **P < 0.001, and ***P < 0.0001; unpaired 2-tailed Student's t test.