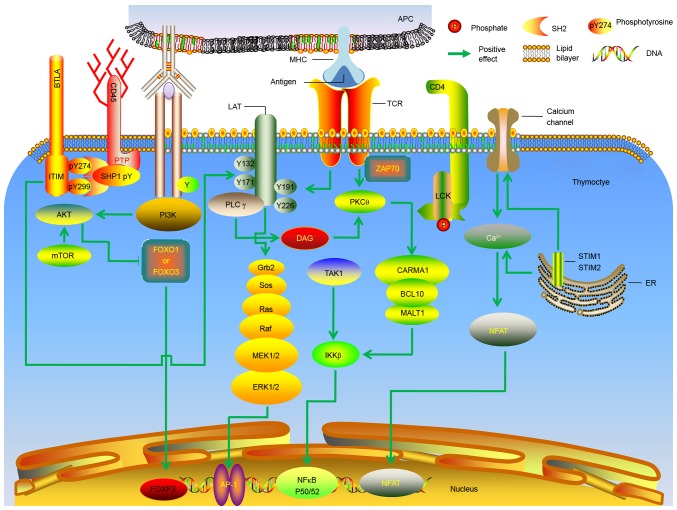
Figure 2.
Molecular mechanisms underlying the generation of thymic regulatory T cells. Molecular signals downstream of the TCR are presented. AP, activator protein; APC, antigen-presenting cell; BCL, B cell lymphoma; BTLA, B and T lymphocyte attenuator; Ca, calcium; CARMA, CARD-containing MAGUK protein; CD, cluster of differentiation; DAG, diacylglycerol; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; IKKβ, inhibitor of nuclear factor κB; ITIM, immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motif; MEK, mitogen-activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; FoxO, forkhead box protein O; FOXP3, forkhead box protein 3; NFAT, nuclear factor of activated T; Grb, growth factor receptor-bound protein; LAT, linker for activation of T cells; LCK, lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase p56; MALT, mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation protein; mTOR, mechanistic target of rapamycin; NF, nuclear factor; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase; PK, protein kinase; PL, phospholipase; PTP, protein-tyrosine phosphatase; Ras, rat sarcoma also known as p21; Raf, rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma; SHP, SH2-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase; SOS, Son of Sevenless; STIM, stromal interaction molecule; TAK, transforming growth factor beta-activated kinase; ZAP70, ζ-associated protein of 70 kD.