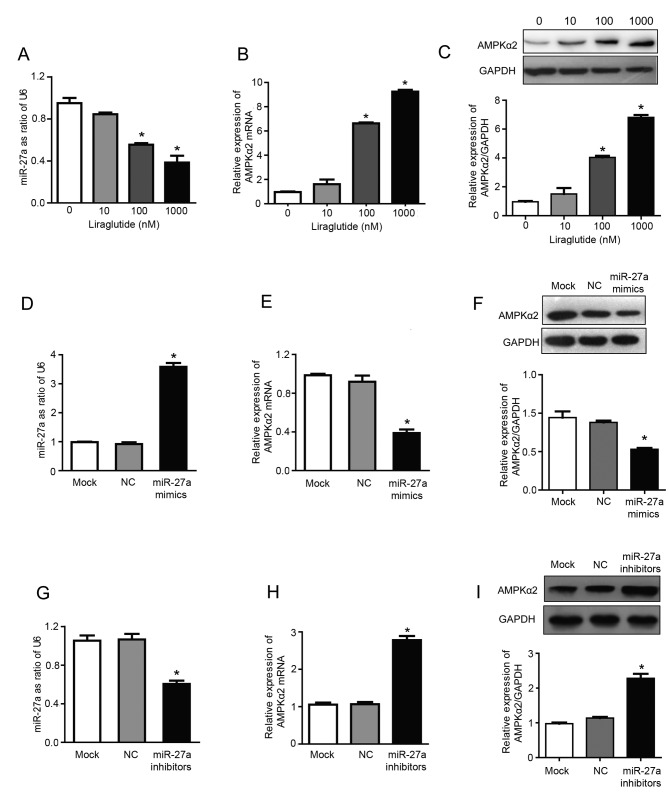
Figure 2.
Liraglutide inhibits miR-27a expression and subsequently upregulates AMPKα2. Following treatment with 10, 100 and 1,000 nM liraglutide for 48 h, RT-qPCR was performed to determine the mRNA levels of (A) miR-27a and (B) AMPKα2. (C) Western blotting was performed to measure the protein levels of AMPKα2. (D) RT-qPCR confirmed that transfection with miR-27a mimics led to the successful overexpression of miR-27a in MCF-7 cells. (E) RT-qPCR demonstrated that the mRNA levels of AMPKα2 were downregulated following transfection with miR-27a mimics. (F) Western blotting demonstrated that AMPKα2 protein expression was downregulated following transfection with miR-27a mimics. (G) RT-qPCR confirmed that transfection with miR-27a inhibitors led to the successful reduction of miR-27 levels in MCF-7 cells. (H) RT-qPCR demonstrated that AMPKα2 mRNA expression was increased following transfection with miR-27a inhibitors. (I) Western blotting demonstrated that AMPKα2 protein expression was increased following transfection with miR-27a inhibitors. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation. For parts A-C, *P<0.05 vs. 0 nM liraglutide; for parts D-I, *P<0.05 vs. NC group. miR, microRNA; AMPKα2, AMP-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit α2; RT-qPCR, reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction; NC, negative control; U6, U6 small nuclear RNA.