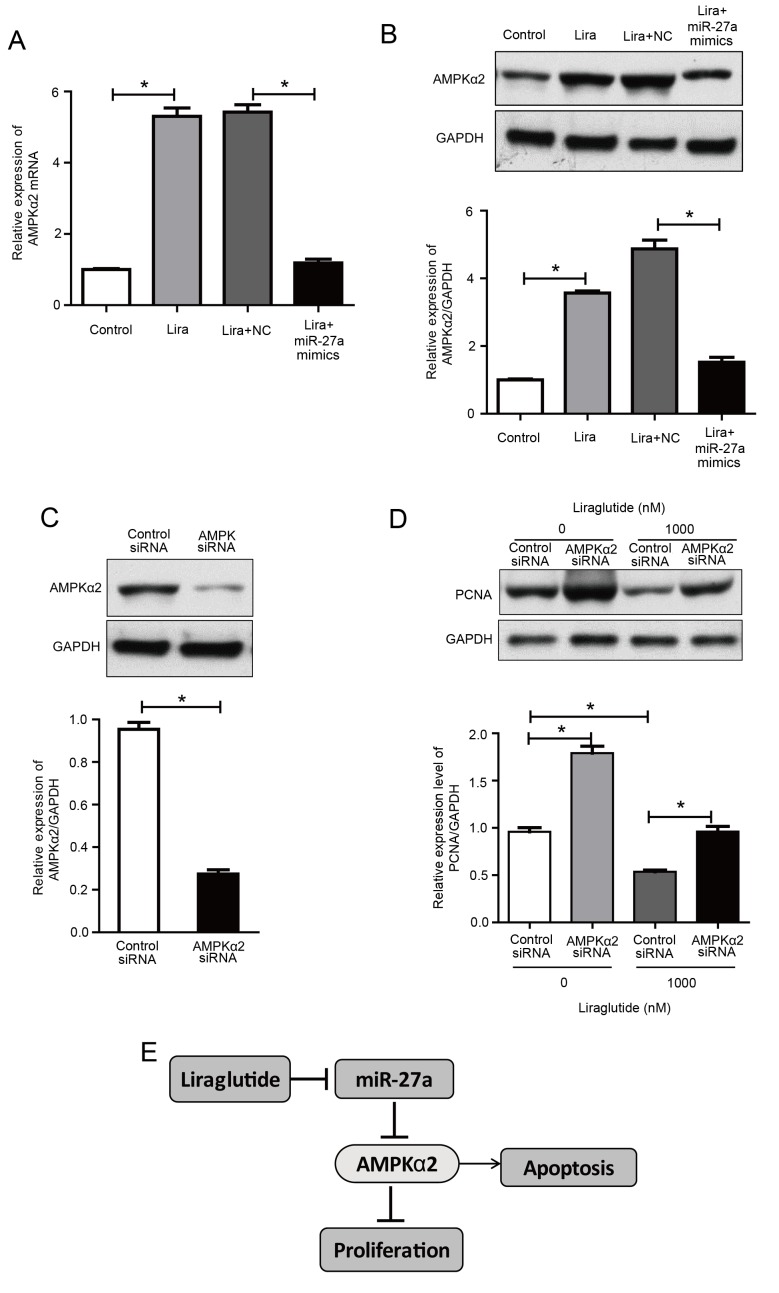
Figure 4.
Upregulation of miR-27a reverses the liraglutide-induced activation of AMPKα2 and AMPKα2 siRNA inhibits liraglutide-induced inhibition of proliferation in MCF-7 cells. (A) AMPKα2 mRNA levels were measured by reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction in MCF-7 cells transfected with or without miR-27a mimics and subsequently treated with liraglutide for 48 h. (B) AMPKα2 protein levels were measured by western blotting in MCF-7 cells transfected with or without miR-27a mimics and subsequently treated with liraglutide for 48 h. (C) MCF-7 cells were transfected with control siRNA or AMPKα2 siRNA for 48 h and western blotting was performed to measure AMPKα2 levels and confirm successful transfection. (D) MCF-7 cells were transfected with AMPKα2 siRNA and cultured with or without 1,000 nM liraglutide for 48 h. The expression of PCNA was determined by western blot analysis. GAPDH served as the loading control. (E) Summary diagram of the regulatory pathway in the present study. In breast cancer cells, liraglutide inhibits miR-27a expression and subsequently activates the AMPK pathway, thereby leading to the induction of cell apoptosis. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation. *P<0.05, as indicated by brackets. miR, microRNA; AMPKα2, AMP-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit α2; siRNA, small interfering RNA; PCNA, proliferating cell nuclear antigen; NC, negative control; Lira, liraglutide.