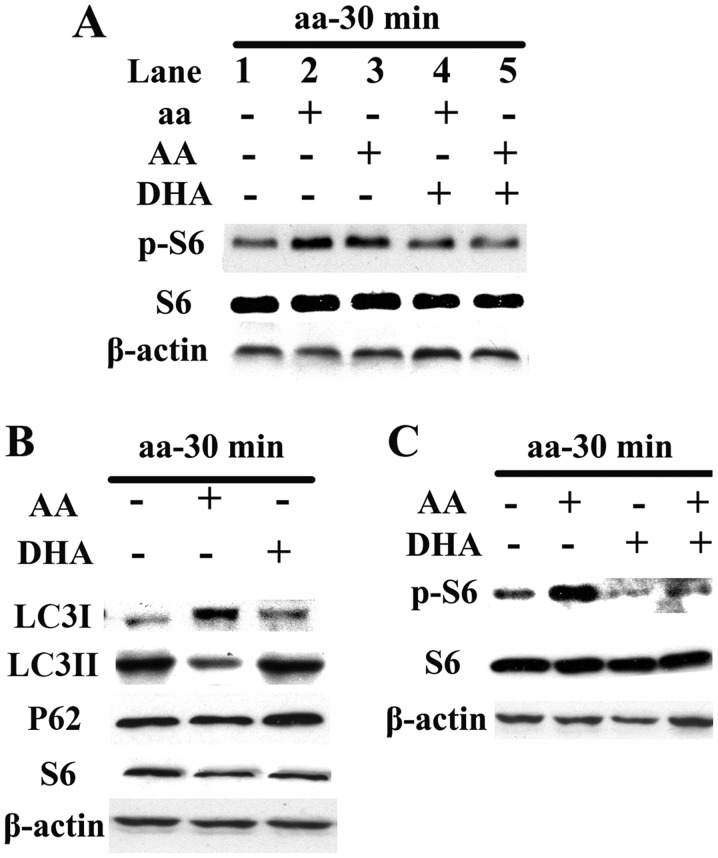
Figure 1.
Effects of exogenous polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) on mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) and autophagy. (A) AA activated mTORC1 independently (lane 1 vs. lane 3), while docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) ameliorated amino acid- and arachidonic acid (AA)-induced activation of the mTORC1 signaling pathway (lane 2 vs. lane 4; lane 3 vs. lane 5). (B) Under amino acid starvation, AA and DHA inhibited and enhanced expression of the autophagic marker LC3-II protein, respectively; the effect on LC3I was opposite to that of LC3-II and the effect on P62 was the same as LC3-II. (C) DHA independently inhibited mTORC1.