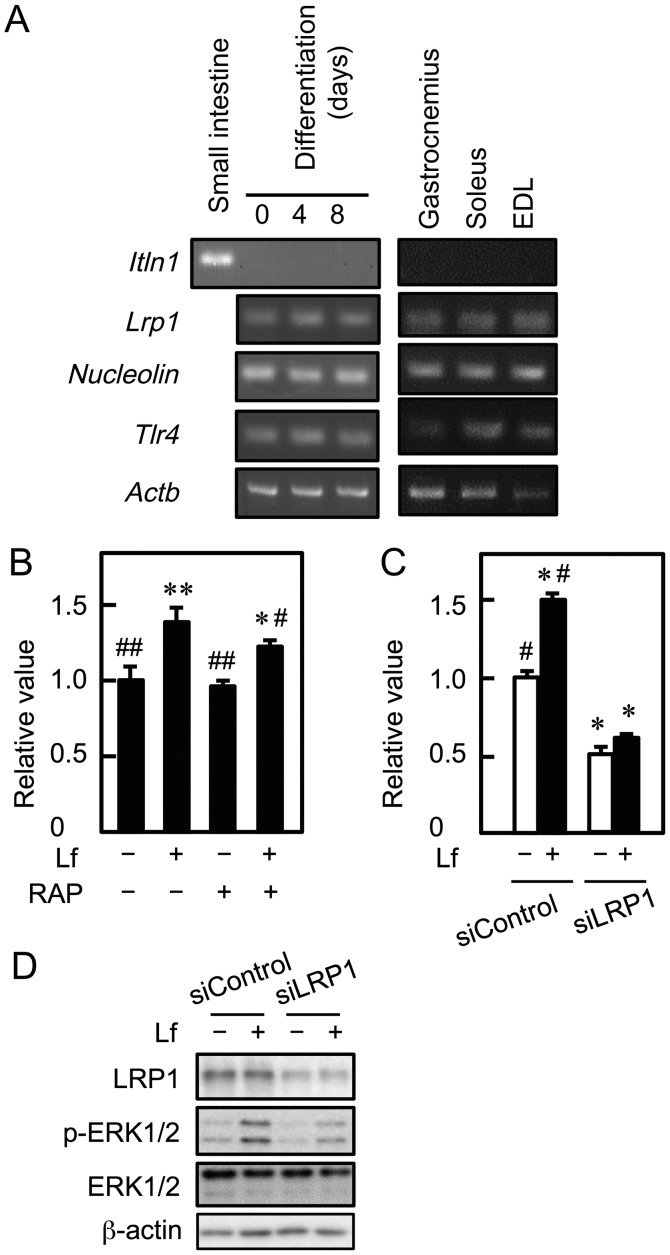
Figure 3.
Involvement of LRP1 in the Lf-promoted proliferation of myoblasts. (A) cDNA was synthesized using total RNA from C2C12 cells, skeletal muscle tissue (gastrocnemius, soleus, and extensor digitorum longus, and small intestine, and was amplified by PCR. (B) Myoblasts were cultured with Lf (25 µg/ml) in the presence of RAP for three days. Cell viability was determined by the alamarBlue assay. Data are expressed as relative values (FI of the experimental group divided by FI of the vehicle group (-Lf, -RAP). Values are indicated as the mean ± SD (n=4). Statistically significant differences were determined by one-way ANOVA and Tukey's post-hoc test. *P<0.01, **P<0.001 vs. vehicle group (-Lf, -U0126). #P<0.05, ##P<0.001 vs. Lf group (+Lf, -RAP). (C) Myoblasts were transfected with control siRNA (siControl) or LRP1 siRNA (siLRP1), followed by culture with Lf for three days. Cell viability was determined by the alamarBlue assay. Data are expressed as relative values (FI of the experimental group divided by FI of the vehicle group (-Lf, siControl)). Values are indicated as the mean ± SD (n=4). Statistically significant differences were determined by two-way ANOVA and Tukey's post-hoc test. *P<0.001 vs. siControl group (-Lf, siControl). #P<0.001 vs. siLRP1 group (-Lf, siLRP1). (D) LRP1 knockdown cells were incubated with Lf for 10 min. The expression of LRP1, ERK1/2, and phosphorylated ERK1/2 (p-ERK1/2) was analyzed by western blotting. Each result is representative of three independent experiments. EDL, extensor digitorum longus; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; Itln1, intelectin 1; Lf, lactoferrin; Lrp1, low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1; RAP, receptor-associated protein; siRNA, small interfering RNA; Tlr4, Toll-like receptor 4; SD, standard deviation; ANOVA, analysis of variance.