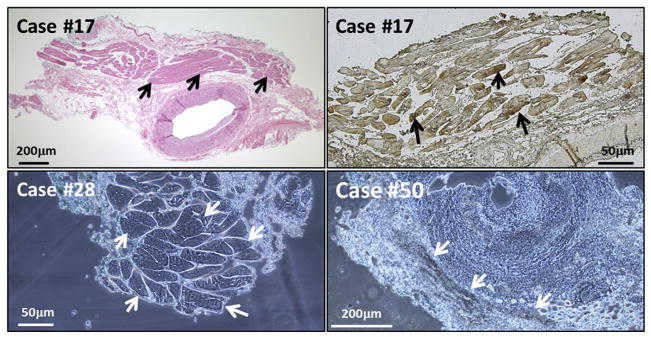
FIGURE 5.
False-positive immunohistochemistry (IHC): extra-arterial skeletal muscle and blood. Two images are included from Case #17, who was giant cell arteritis negative. (Top left) Hematoxylin-eosin stain of a temporal artery (TA), to show region with extra-arterial skeletal muscle (arrows). (Top right) False-positive IHC result when incubated with MAb 3B3 and observed with the Olympus microscope with dry mount (black arrows). There was no varicella-zoster virus–positive staining within any region of the temporal artery itself. (Bottom left) False-positive stain of skeletal muscle from Case #28. The TA specimen was incubated with only the color reagents in the IHC assay; neither primary nor secondary antibody was added. The false-positive result in the skeletal tissue is marked by white arrows. (Bottom right) False-positive attachment of anti-reovirus antibody to erythrocytes within the TA biopsy samples (white arrows). Scale bars are shown in each image.