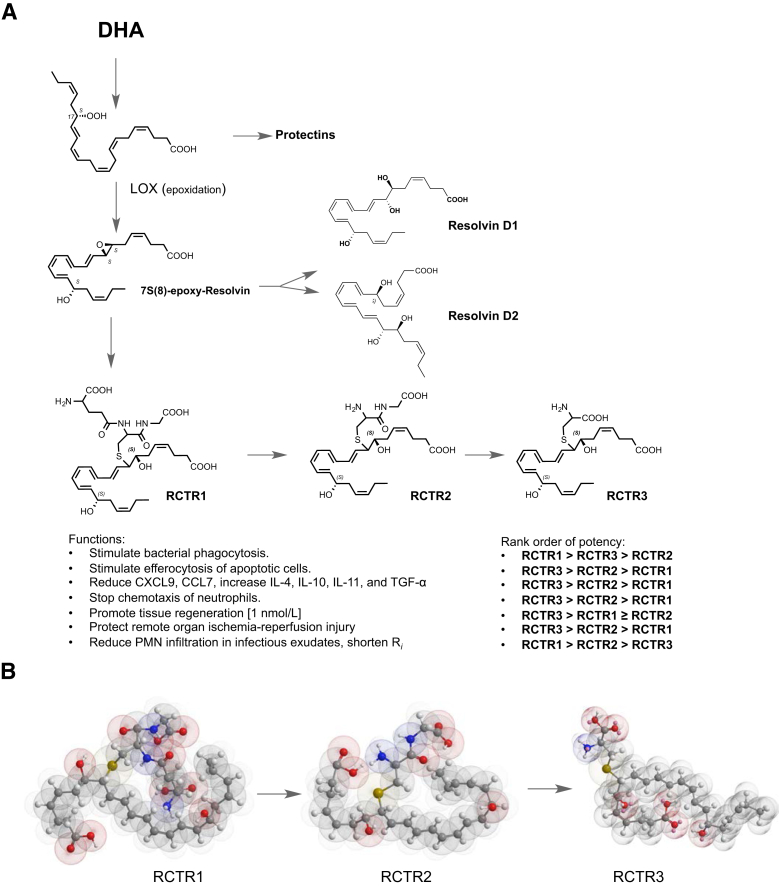
Figure 8.
Biosynthesis, stereochemistry, and RCTR functions. A: DHA is converted via lipoxygenase to the 17-hydroperoxy intermediate to produce protectins2 or can undergo a second lipoxygenation (namely, hydrogen abstraction with insertion of molecular oxygen) at the carbon-7 position, yielding 7S,17S-dihydro(peroxy)-4Z, 9E,11E,13Z,15E,19Z-docosahexaenoic acid, which is enzymatically converted to an allylic epoxide, followed by production of RCTR1.17 This glutathionyl conjugate can be converted to RCTR2 and subsequently to RCTR3. Complete stereochemistry of each bioactive RCTR is determined herein and is as shown. Functions of RCTRs in human phagocytes, mouse, and planaria were determined, and rank-order potencies were established. B: Structures in three-dimensional configuration using energy minimization (ChemBio3D Ultra 14.0; PerkinElmer, Cambridge, MA) for RCTR1, RCTR2, and RCTR3. Each gave distinct overall three-dimensional structures that may relate to their separate actions and rank orders in potencies.