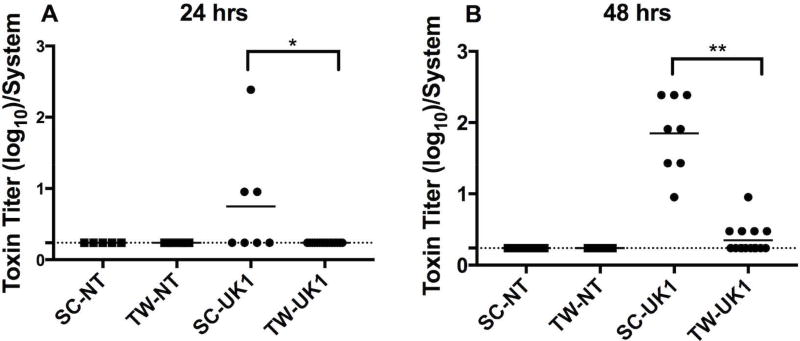
Figure 3. A significantly higher toxin activity detected in 3D scaffolds compared to 2D transwells.
Toxin activity was measured by a MEF cell rounding assay. Serial three-fold dilutions of supernatants from 3D scaffolds (SC) or 2D transwells (TW) infected with NT or UK1 C. difficile spores for (A) 24 hrs or (B) 48 hrs were applied to MEF cells for 24 hrs and scored visually at 10× magnification for 100% cell rounding. The log of the inverse of the highest dilution that produced 100% cell rounding of the MEF cells is plotted. Each dot represents the result from an individual scaffold or transwell; the horizontal bars indicate the mean; the horizontal dashed line indicates the limit of detection. Statistical significance between the supernatants from the SC and TW for each strain at each time point was determined by the Mann-Whitney t-test (*p=0.02, and **p<0.0001).