Figure 9.
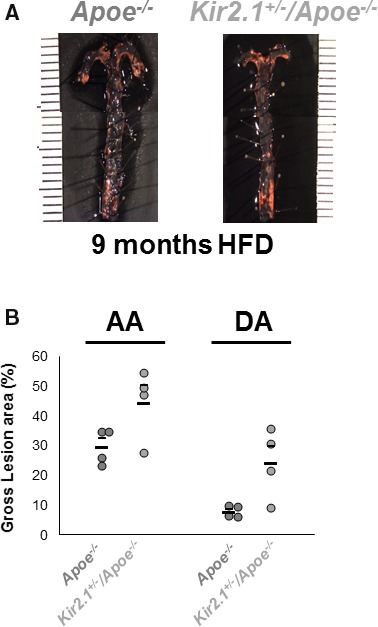
Inwardly rectifying K+ (Kir) 2.1 deficiency promotes the formation and alters the distribution of atherosclerotic lesions in mouse aortas. A, Representative images of en face aortas from apolipoprotein E–deficient (Apoe −/−; left) and Kir2.1 +/− /Apoe −/− (right) stained with Oil Red O for lesion detection. Mice were fed a Western, high‐fat, high‐cholesterol diet (HFD) for 9 months before analysis. Aortas were isolated into the thoracic region immediately before the diaphragm. B, Group analyses of the lesions detected show lesion formation in the aortic arch (AA) and descending aorta (DA) as measured as percentage of the total area containing lesions. Larger, lower bars represent the group average and smaller, upper bars represent the standard error. For all groups, n=4. Significance was tested using 2‐way ANOVA. P<0.05 when comparing Apoe −/− and Kir2.1 +/− /Apoe −/−.
