Fig. 1.
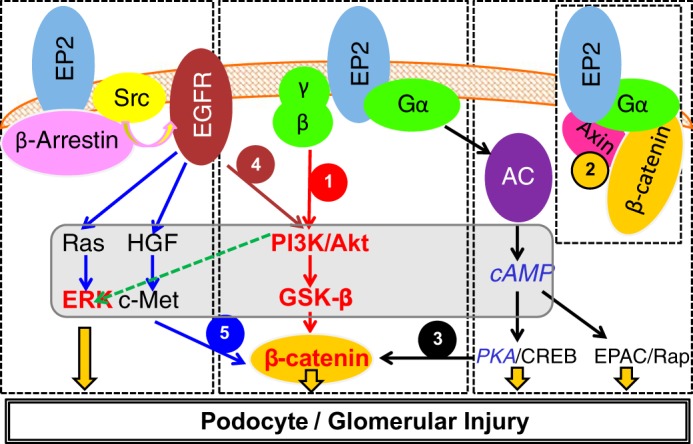
A compiled summary of signaling pathways activated by prostanoid receptor PGE2 receptor 2 (EP2) in osteocytes, neurodegenerative diseases, and colon cancer (see text for details). EP2 is a G protein-coupled receptor that activates the heterotrimeric Gs (αβγ) protein. β-Catenin can be recruited by EP2-mediated signaling by 1) phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt/GSK3β, which preferentially phosphorylates β-catenin at Ser552, 2) binding of the Gα complex to axin and release of β-catenin from the axin-β-catenin-GSK3β complex, 3) generation of cAMP by adenylate cyclase (AC) and activation of PKA, which preferentially phosphorylates β-catenin at Ser675, 4) recruitment by EP2 of β-arrestin 1 and phosphorylation of Src-kinase, which then transactivates the EGF receptor (EGFR) signaling network of PI3K/Akt, and 5) the hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)/tyrosine-protein kinase Met (c-Met) pathway. The study found Akt-GSK3β-β-catenin and ERK (shown in red and bold font), but not cAMP-PKA (shown in blue and italic font), to be important in mechanotransduction. CREB, cAMP-response element-binding protein; EPAC, exchange protein directly activated by cAMP; Rap, Rap GTP-binding protein.
