Fig. 9.
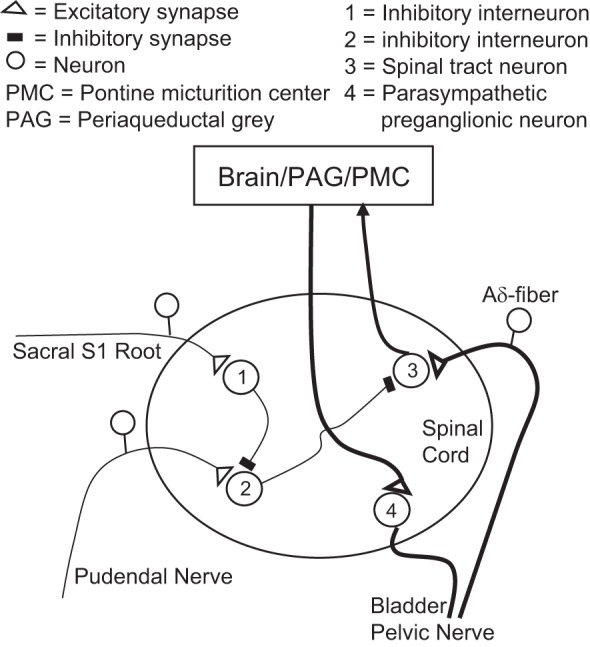
Hypothetical spinal mechanisms that underlie: first, the inhibition of the micturition reflex pathway by afferent axons in the pudendal nerve, and second, the suppression of the pudendal afferent inhibitory pathway by electrical stimulation of the sacral S1 dorsal root. Pudendal afferents activate an inhibitory interneuron (2) that suppresses activity of a spinal tract neuron (3) on the ascending limb of the micturition reflex. S1 dorsal root stimulation activates an inhibitory interneuron (1) that suppresses activity of the interneuron (2) in the pudendal afferent inhibitory pathway.
