Fig. 1.
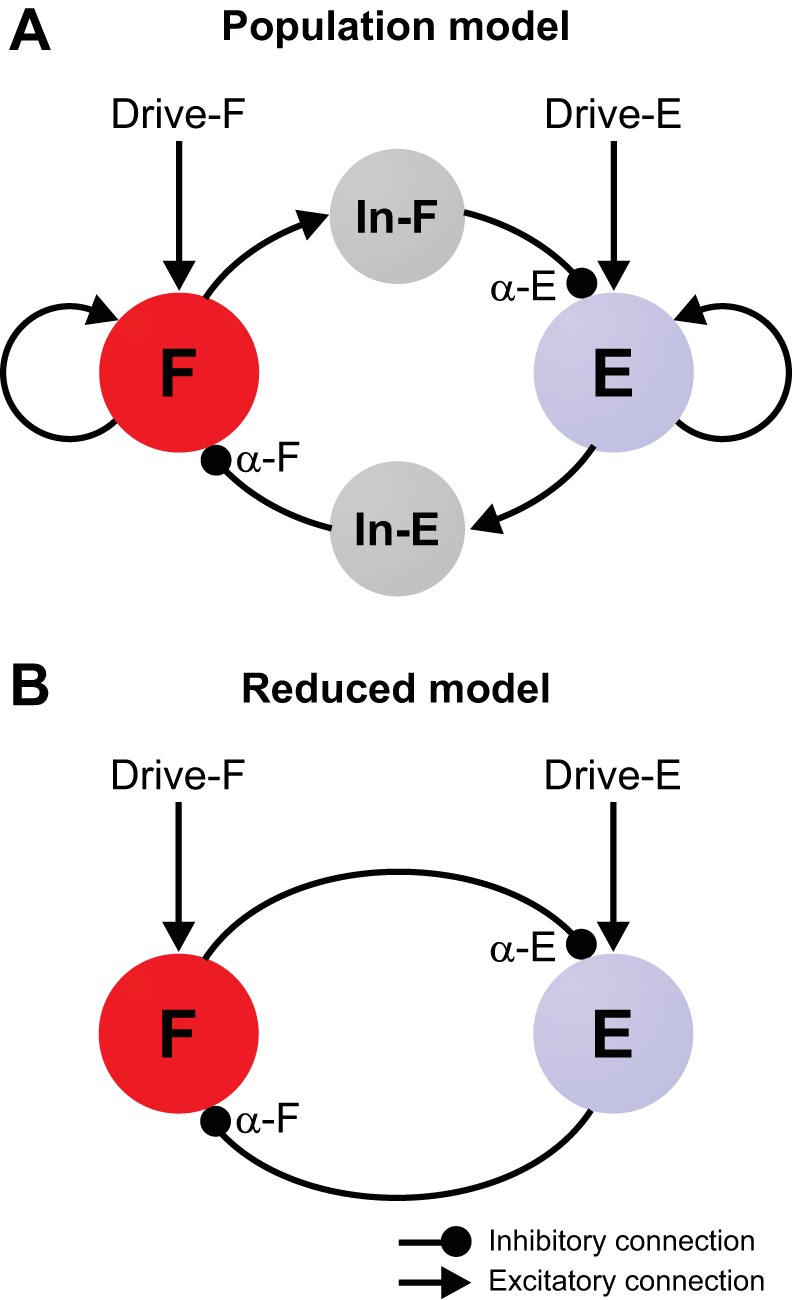
Model schematics. A: in the population model, the flexor (F) and extensor (E) half-centers represent populations of 200 neurons with INaP-dependent bursting properties and sparse mutually excitatory interconnections. These half-centers inhibit each other via corresponding populations of inhibitory neurons (In-E and In-F) each consisting of 100 neurons. α-F and α-E denote the overall strength of the mutual inhibition to each flexor and extensor neuron, respectively. Each half-center receives tonic external drive (Drive-F/E). All neurons are modeled in the Hodgkin-Huxley style (see methods). B: in the reduced model, the flexor and extensor half-centers are represented by two activity-based (nonspiking) units that mutually inhibit each other.
