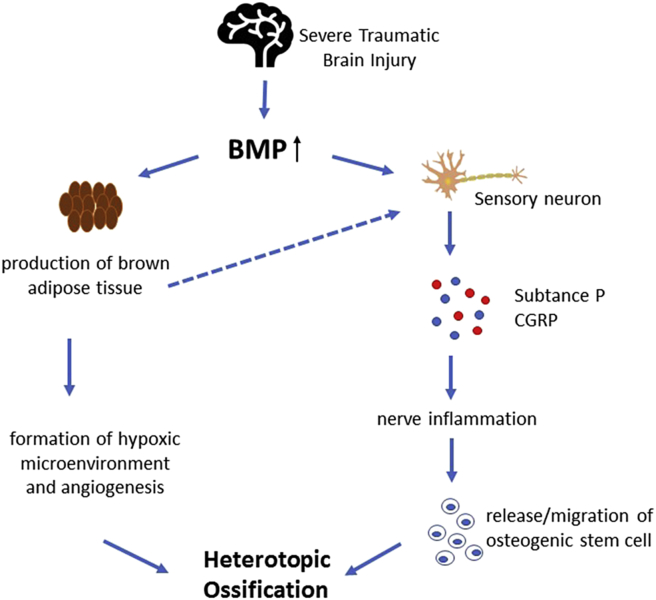
Figure 1.
An overview of the function of BMP on TBI–HO. After brain injury, the levels of BMP and its receptor, as well as the expression of its mRNA, are all upregulated. BMP subsequently acts on sensory neurons, induces the release of inflammatory cytokines, substance P and CGRP, and causes nerve inflammation, leading to nerve regeneration and migration or release of osteogenic stem cells or other stem cells. Abnormally elevated levels of BMP also induce the production of BAT, promoting the formation of hypoxic microenvironment and angiogenesis, generating heat and stimulating the sensory neurons to release SP and CGRP. BMP = bone morphogenetic protein; BAT = brown adipose tissue; CGRP = calcitonin gene-related protein; HO = heterotopic ossification; SP = substance P; TBI = traumatic brain injury.