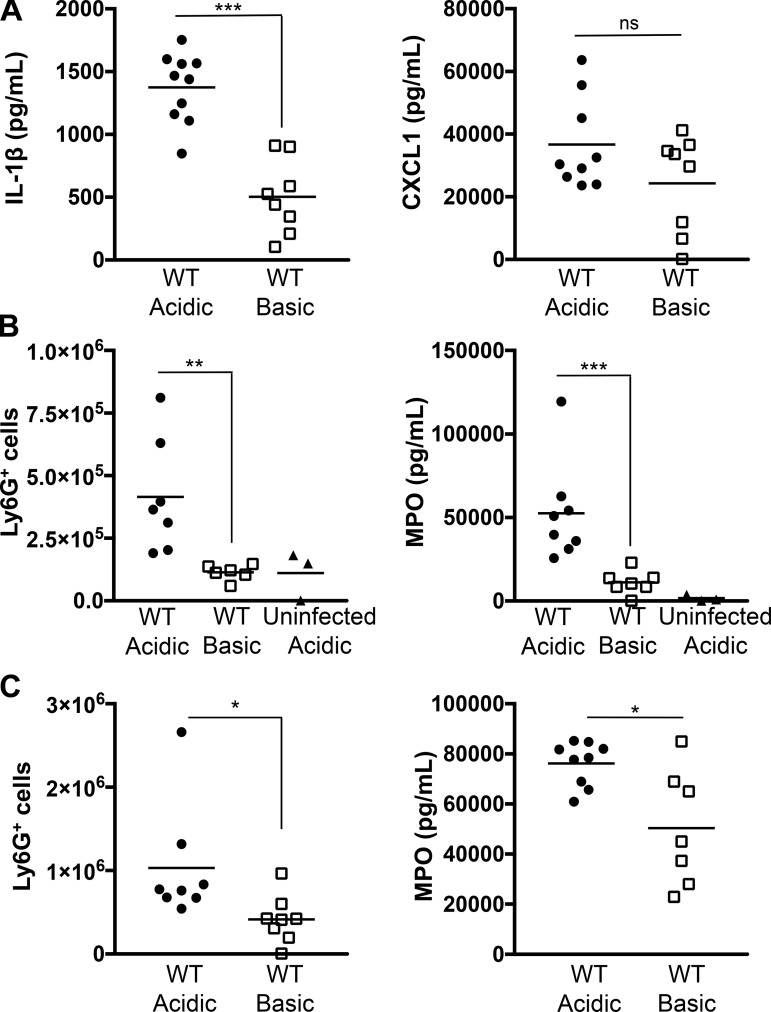
Fig. 3.
Acidosis enhances neutrophil recruitment in a pneumonia model of P. aeruginosa infection. C57BL/6 mice were infected intratracheally with 3 × 106 CFU of WT PA14 in an acidic or a basic pH buffer, and bronchoalveolar lavage samples were collected. A: IL-1β and CXCL1 production was analyzed by ELISA at 6 h postinfection. B and C: neutrophil recruitment and activation were determined at 3 h (B) or 6 h (C) postinfection by quantification of pulmonary Ly6G+ cells by flow cytometry and myeloperoxidase (MPO) levels by ELISA. Data are derived from 3 independent experiments (n ≥ 6 for all test groups except uninfected acidic, in which n = 3). ***P ≤ 0.0005; **P ≤ 0.005; *P ≤ 0.05; ns, not significant [by unpaired Student’s t-test with Welch’s correction (A and C) or 1-way ANOVA with Sidak’s post hoc analysis (B)].