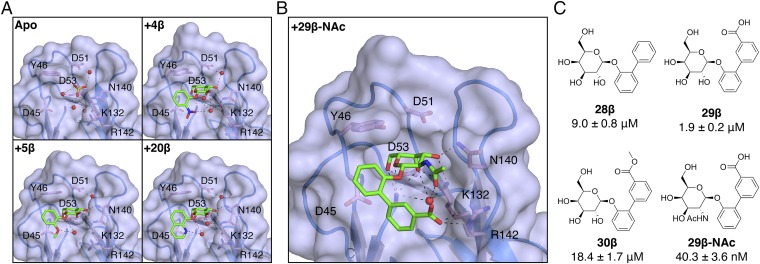
Fig. 4.
Structural basis of galactoside inhibition of FmlHLD. (A) Crystal structures of sulfate ions or galactosides bound in the FmlHLD binding pocket, with H-bonding (black dashed lines) indicated between sulfate ions (yellow sticks), ligands (green sticks), water molecules (red spheres), or side chains (pink sticks). Crystal structures shown here include an apo FmlHLD crystal structure (PDB ID 6AOW), a FmlHLD-4β cocrystal structure (PDB ID 6ARM), a FmlHLD-5β cocrystal structure (PDB ID 6ARN), and a FmlHLD-20β cocrystal structure (PDB ID 6ARO). (B) Cocrystal structure of 29β-NAc bound to FmlHLD (PDB ID 6AS8). (C) SARs for 29β-NAc and related compounds, with their corresponding IC50 values derived from the ELISA-based competition assay. IC50 values are reported for six replicates as the mean with SEM.