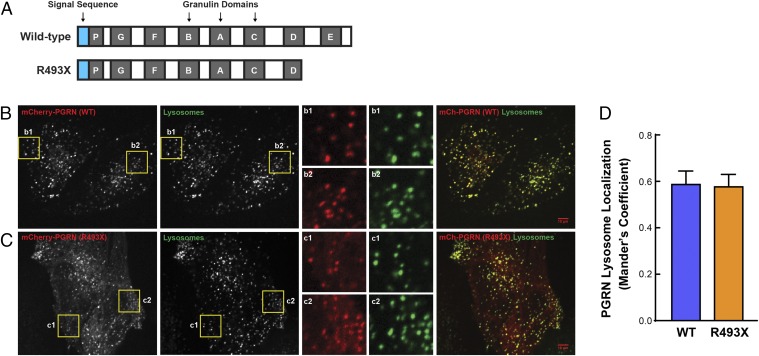
Fig. 5.
Progranulin R493X mutant is delivered to lysosomes. (A) Schematic representation of the wild-type progranulin and the R493X truncated mutant proteins. Blue boxes, signal sequence; gray boxes, granulin domains. (B and C) Images show the colocalization of mCherry-PGRN wild-type (B) and mCherry-PGRN R493X (C) with Alexa Fluor 647-dextran–labeled lysosomes in progranulin-deficient HeLa cells. Inset boxes (b1, b2, c1, and c2) obtained from the highlighted regions show the robust overlap of mCherry-PGRN puncta with lysosomes. (Scale bars, 10 μm.) (Magnification: B and C, Insets, 3×.) (D) Quantitative colocalization analysis shows similar lysosome localization for both wild-type and R493X forms of progranulin. Colocalization coefficient was quantified on a per cell basis, and 22–28 transfected cells were measured for each plasmid. Data are presented as mean ± SEM from four independent experiments. P = 0.897 (nonsignificant), as determined by unpaired t test.