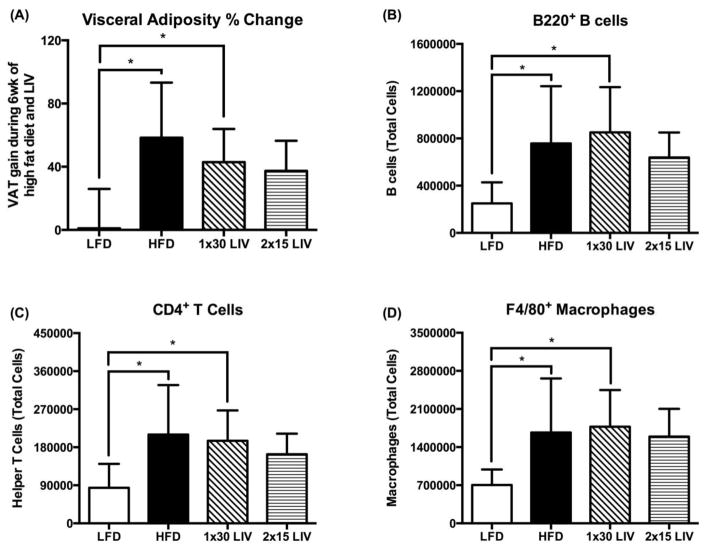
Figure 2.
Visceral adiposity and infiltration of immune cells in gonadal adipose tissue in a murine model of diet-induced obesity (45% kcal from fat diet) in adult male C57BL/6J mice. All mice were fed their respective diets for 2wk, followed by 6wk of low intensity vibration (LIV; 90Hz, 0.2g peak acceleration (g = Earth’s gravitational force), 5d/wk) treatment, while continuing on high fat diet. Continued gain in visceral adiposity with high fat diet feeding in HFD and 1×30 LIV group, which was prevented with 2×15 LIV (A). Increased infiltration of B cells (B), T cells (C), and macrophages (D) in gonadal adipose tissue with high fat diet, which was mitigated by 2×15 LIV, but not 1×30 LIV. *p<0.05. All data are presented as mean±SD. (Figure modified from [5]). Used with permission from Nature Publishing.