Figure 8.
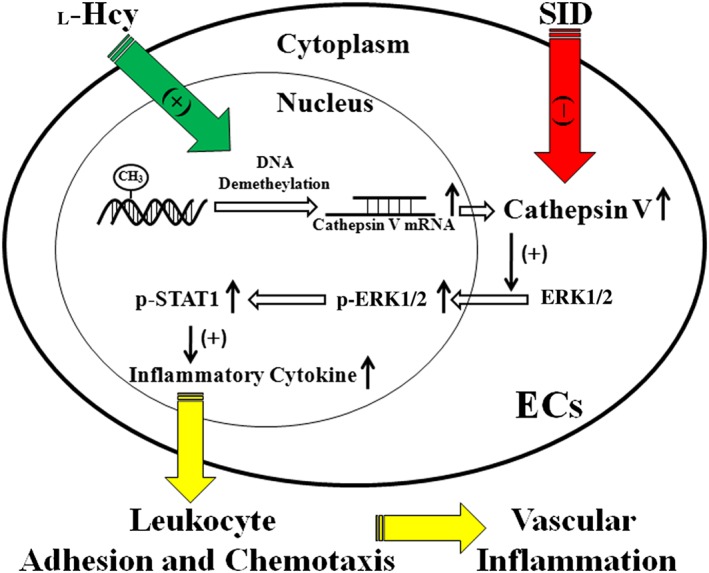
Schema of hypothesis that l‐Hcy stimulates intracellular cathepsin V expression via a DNA demethylation pathway. Increased cathepsin V promotes the phosphorylation and subsequent nuclear translocation of ERK1/2, phosphorylation of STAT1, expression of inflammatory cytokines, adhesion and chemotaxis of leukocytes and vascular inflammation. The cathepsin L/V inhibitor SID suppresses the activity of cathepsin V, and reverses the up‐regulation of inflammatory cytokines and vascular inflammation induced by l‐Hcy.
