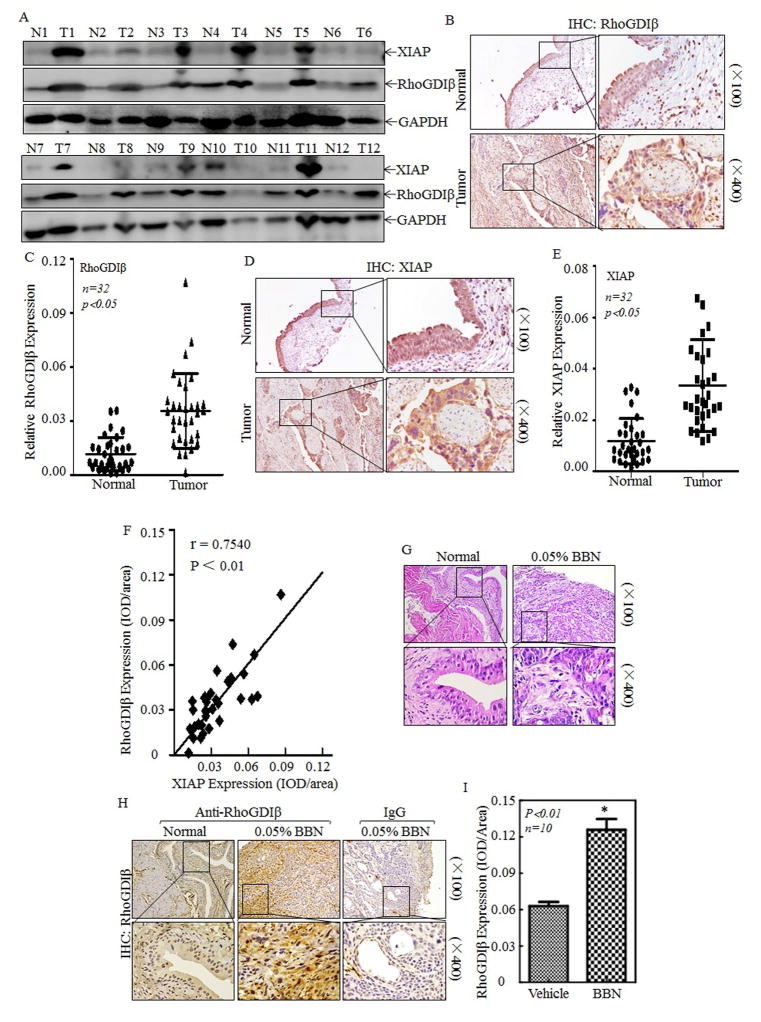
Figure 1. RhoGDIβ was overexpressed in BC of human patients and BBN-induced mice.
(A) Total protein lysates were prepared from the cancerous (T) and their paired adjacent normal (N) tissues of human BC patients were collected as described in “Methods”, the total proteins were extracted and then subjected to Western blotting analyses, and specific antibodies against XIAP and RhoGDIβ were used to determine the level of XIAP and RhoGDIβ proteins. (B–F) Rho-GDIβ and XIAP proteins level was evaluated by using IHC staining in bladder cancer tissues in comparison to the paired normal bladder tissues (n=32). IHC images were captured under microscopy. (B&D), and the quantitative (C&E) and correlation of XIAP expression with RhoGDIβ level was analyzed and presented (F). (G–I) Upon 23 weeks treatment of mice with or without BBN, the bladder tissues from indicated mice were pathologically analyzed by H&E staining (G) and by IHC staining to evaluate RhoGDIβ expression (H). Homotypic IgG was used as negative control (H) and the optical density was calculated as described in “Methods” (I). The results were presented as mean ± SD from at least triplicate experiments and asterisk (*) indicated a significant difference (P<0.05)