Figure 4. XIAP regulated nucleolin mRNA stability in Erk-dependent manner.
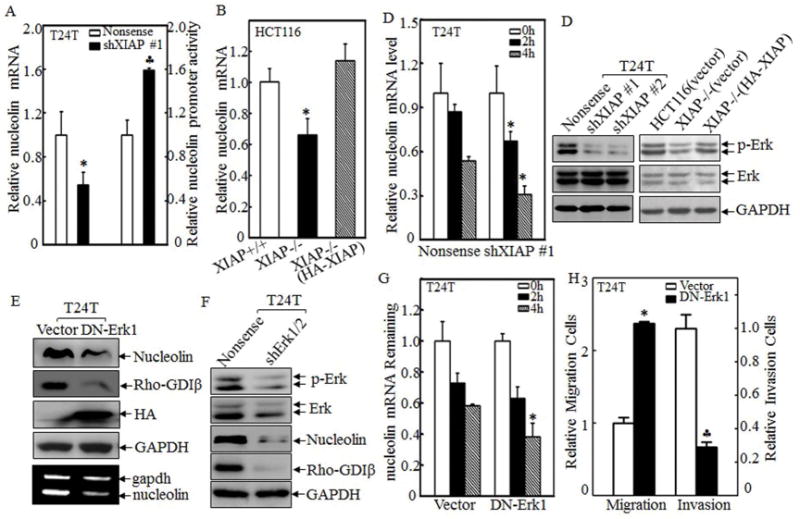
(A&B) The nucleolin mRNA expression was evaluated in paired T24T/nonsense and T24T/shXIAP transfectants (A, left panel) or XIAP+/+, XIAP−/−(vector) and XIAP−/−(HA-XIAP) cells (B) by real-time PCR assay. Nucleolin promoter-driven luciferase reporter and pRL-TK was transiently co-transfected into T24T cells as indicated, and then the luciferase activity was evaluated (A, right panel). (C) T24T transfectants as indicated were seeded into 6-well plate and cultured till 75–80% confluence. The cells were then treated with 5μM of Act D for indicated time periods, Real-time PCR assay was employed to analyze the stability of nucleolin mRNA. (D) The cell extracts of T24T and HCT116 cell transfectants as indicated were subjected to Western blotting for determination of Erk phosphorylation. (E&F) The plasmid of HA-tagged DN-Erk1, shErk1/2, and their control vectors were transfected into T24T cells. The cell extracts were subjected to Western Blotting using specific antibodies as indicated and total RNA from the transfectants was used to determine nucleolin mRNA levels by using RT-PCR assay. (G) T24T transfectants as indicated were seeded into 6-well plate and cultured till 75–80% confluence. The cells were than treated with 5μM of Act D for indicated time periods. Real-time PCR assay was employed to analyze the stability of nucleolin mRNA. (H) Cell migration (left panel) and invasion (right panel) of transfectants was evaluated and quantitated by using transwell assay. All the results were presented as mean ± SD from three independent experiments and the asterisks (*), (♣) indicated a significant difference (P <0.05).
