Figure 1. TASC validity.
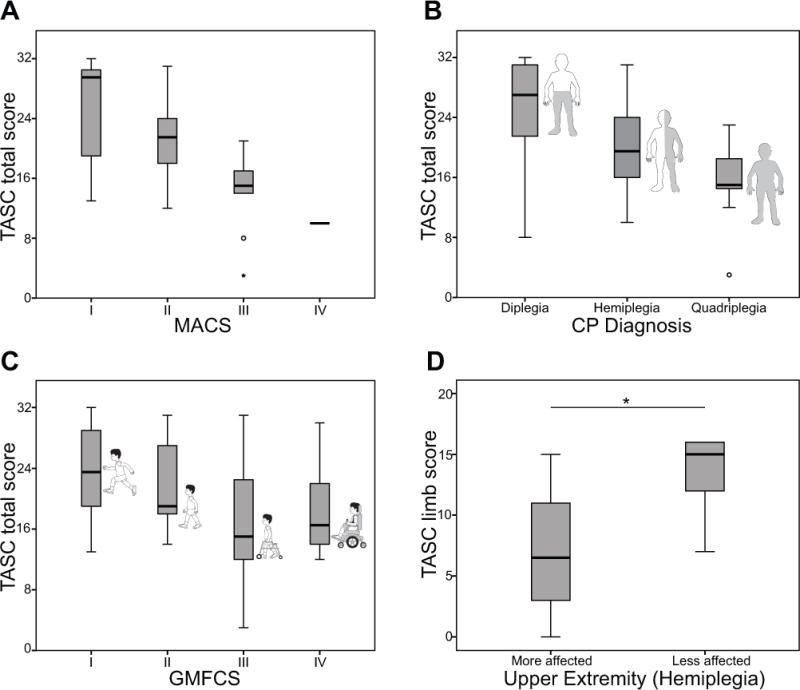
(a) Boxplot of total TASC scores by MACS classification. There was a correlation between MACS level and TASC score (r=−0.529, p<0.001), demonstrating concurrent validity with an activity measure. (b) Boxplot of total TASC scores by limb distribution, or the total number of upper extremities affected according to diagnosis. This was correlated to the total TASC score (r=−0.486, p=0.001). (c) Boxplot of total TASC scores by GMFCS classification. GMFCS level demonstrated a weak correlation to the TASC score (r=−0.362, p=0.006). (d) Discriminate validity between more and less affected limbs in hemiplegia. *Indicates significant (p<0.001) difference between the TASC limb score between sides. TASC, Test of Arm Selective Control; MACS, Manual Ability Classification System; CP, cerebral palsy; GMFCS, Gross Motor Functional Classification System.
