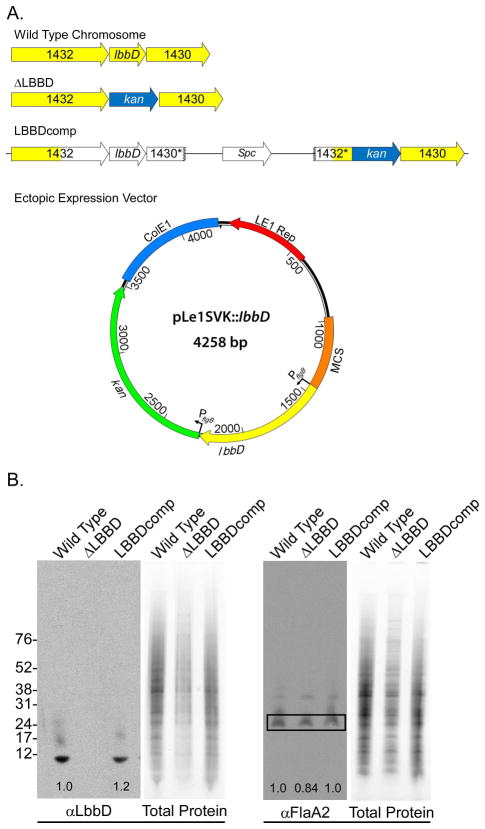
Fig. 2. Genetic structure and protein production of bactofilins from wild type and mutant strains.
A. Genetic structure of the wild type, lbbD mutant, complement, and SV1LBBD (ectopic expression of lbbD). In the complementation strain, LBBDcomp, the yellow-colored arrows represent chromosomal loci and open arrows denote DNA derived from integration of the E. coli complementation vector. * indicates partial genes formed by the insertion of the complementing plasmid. The shuttle vector expressing lbbD contains both a leptospiral (LE1 Rep) and an E. coli (ColE1) origins of replication, both lbbD (yellow arrow) and the kanamycin-resistance cassette (green arrow) are fused to borrelial flgB promoters. MCS, multiple cloning site
B. Quantitation of LbbD and FlaA2 levels in L. biflexa strains. Antiserum against purified LbbD and FlaA2 was used in quantitative immunoblots standardized to the total protein load of each lane and the results are shown as numbers (relative to wild type levels) at the base of each blot.