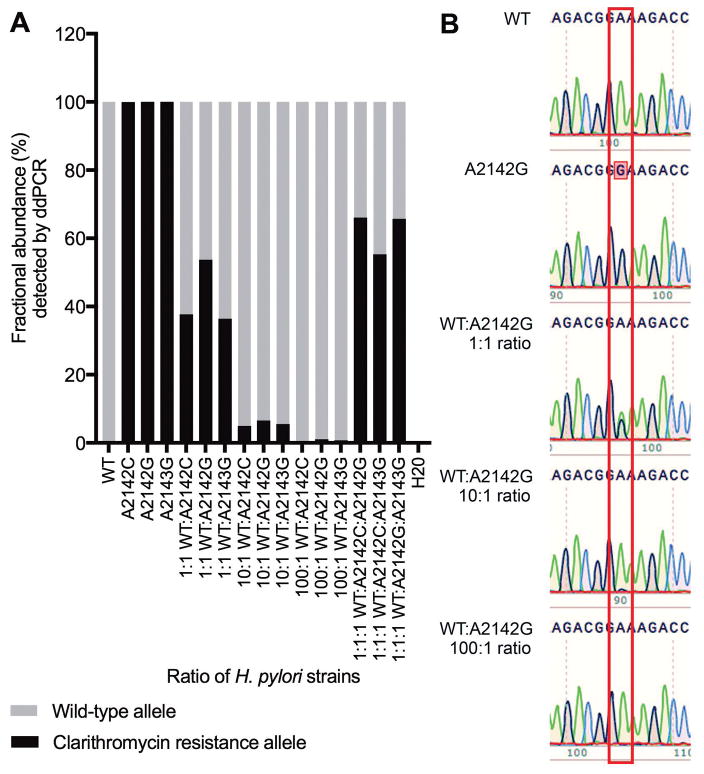
Figure 1.
Detection of clarithromycin resistance alleles by ddPCR assay (A) and Sanger sequencing (B). DNA from H. pylori strains with different 23S rRNA gene alleles was spiked into water individually and in different ratios as indicated. A: Fractional abundance (%) of wild-type and clarithromycin resistance alleles detected by ddPCR assay. B: Chromatogram from Sanger sequencing of 23S rRNA gene PCR amplicon from water spiked with H. pylori DNA from wild-type and resistant strains (A2142G, A2142C, and A2143G) at the ratios indicated. A box is drawn around position 2142 of the H. pylori 23S rRNA gene: adenosine green peaks, guanosine black peaks. Data is representative of three independent experiments.