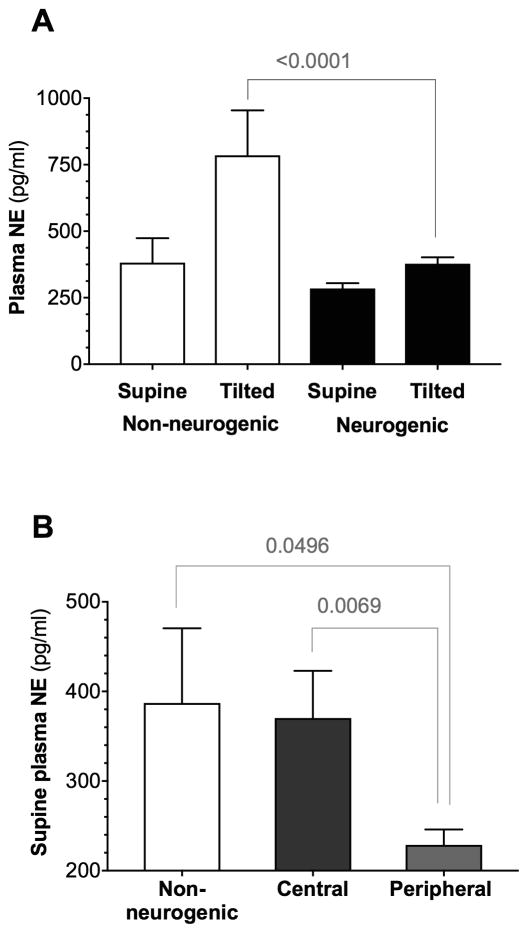
Figure 2. Norepinephrine profiles in neurogenic and non-neurogenic orthostatic hypotension.
A. Plasma norepinephrine levels supine and after 10 minutes of upright tilt in patients with neurogenic vs. non-neurogenic orthostatic hypotension (OH). Note the preserved increase (~ Δ100%) in plasma norepinephrine levels in patients with non-neurogenic OH, indicating intact baroreflex-mediated sympathetic activation. B. Supine plasma norepinephrine levels in central and peripheral autonomic failure compared to non-neurogenic OH. Norepinephrine levels were lowest in patients with peripheral lesions (i.e., Parkinson disease, dementia with Lewy bodies, and pure autonomic failure), indicating severe involvement of post-ganglionic sympathetic neurons in this group. Differences assessed with ANOVA.