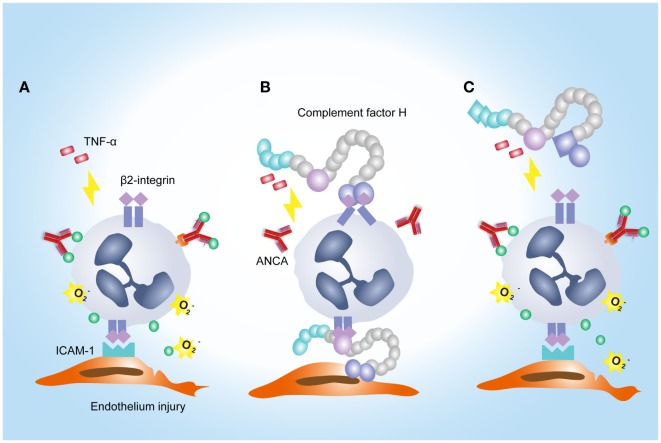
Figure 7.
A proposed model of factor H (FH)–neutrophil interaction in the pathogenesis of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAV). (A) TNF/β2-integrin joint signals triggers explosive responses of neutrophils adherent to endothelial cells in the presence of ANCA, resulting in degranulation and oxidative burst of neutrophils. (B) Binding of FH on neutrophils through β2-integrin inhibits ANCA-induced activation of neutrophils. (C) In AAV, FH is deficient in binding neutrophils and inhibiting neutrophil activation by ANCA, which may be partly related to tyrosine nitration and chlorination of FH and genetic variations of FH.