Figure 5.
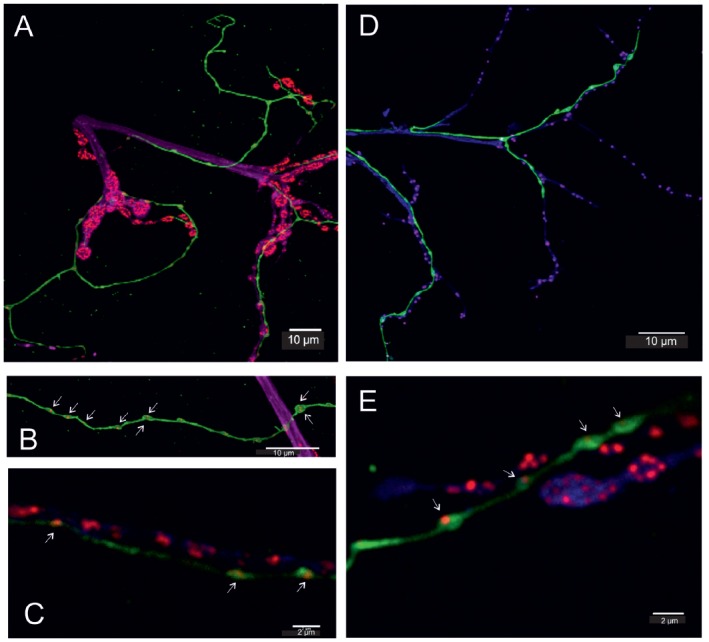
Fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) larva (A–C) and adult (D,E). (A–C) In transgenic flies (TDC2-gal4 × UAS-CD8-GFP, green) all VUM-neuron axons are labeled in green. Additionally, motor axons of body wall muscles are labeled by anti-Horseradish peroxidase (HRP) in magenta/blue and active zones of synaptic sites of the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) are labeled by BRPNC82 (“anti-bruchpilot”) in red and are adjacent to the GFP-labeled (green) octopaminergic axons (A). In the GFP-labeled octopaminergic fibers one or two BRP-labels are revealed in each bouton (varicosities in B,C, white arrows), and in (C) red BRP-labeling is also seen in the motor axon. (D,E) In the adult DLM flight muscle (FM) the axons of motor neurons are labeled by anti-HRP (blue) and again show their relationship to the VUM-neuron fiber stained in green and the red labels of the active zones. The structure of the NMJ of adult muscle differs from that of larval muscle, particularly good to see in (E). However, the octopaminergic VUM-fiber like in larvae reveals one (or two) BRP-spots (punctae) in each bouton (varicosity). Scale bars: (A,B,D): 10 μm, (C,E): 2 μm.
