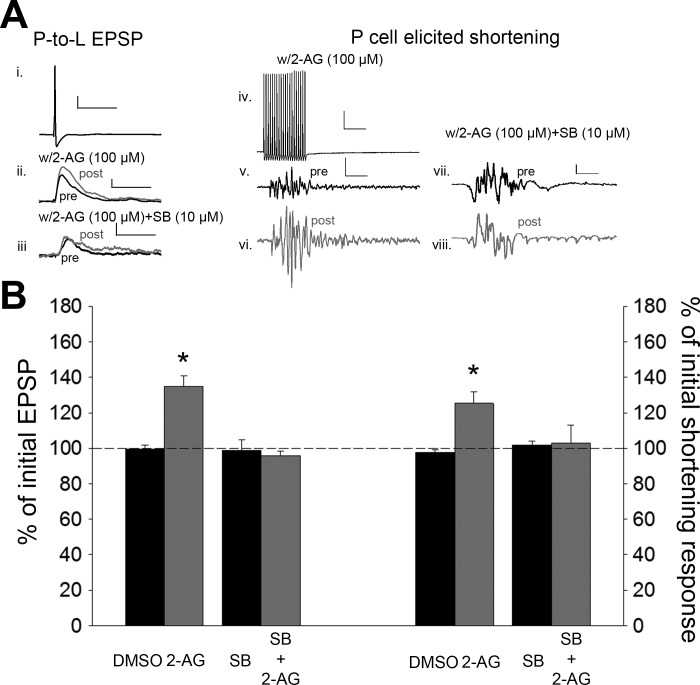
Fig. 3.
2-Arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG) potentiates the nonnociceptive P-cell synapses and P cell-elicited shortening. A: sample recording of P-cell action potential (i; scale bar: 20.0 mV, 50 ms) and the EPSPs elicited before and after bath application of 2-AG (ii; scale bar: 2 mV, 50 ms) or 2-AG + SB (iii; scale bar same as ii) and sample recording of the train of P-cell action potentials used to elicit shortening (iv; scale bar: 20.0 mV, 50 ms) and the shortening responses following treatment with either 2-AG (v and vi; scale bar: 2 mV, 50 ms) or 2-AG + SB (vii and viii; scale bar: 2.0 mV, 50 ms). Black and gray traces are pre- and posttest recordings, respectively. B: average ± SE changes in EPSP amplitude (left) and magnitude of the shortening response (right) (in both cases, y-axis represents % of pretest amplitude) following vehicle (DMSO), 2-AG, or SB + 2-AG (left). *Statistically significant difference compared with controls based on a 1-way ANOVA with Student-Newman-Keuls post hoc test (see results). n = 5 for all treatment and control groups.