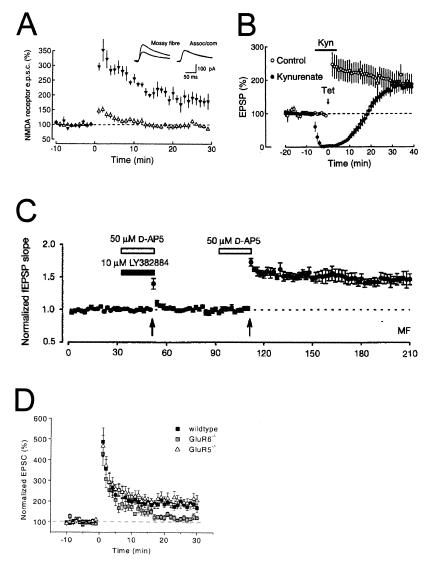
Figure 9.
Evidence for and against the involvement of KARs in mossy fiber LTP. (A) Mossy fiber NMDAR EPSCs are recorded at >+30 mV in the presence of 10 μM CNQX. Tetanization at time = 0 induces mossy fiber LTP (▴), but does not induce LTP at neighboring associational/commissural synapses (▵). [Reprinted with permission from ref. 27 (Copyright 1995, MacMillan Magazines Ltd., www.nature.com).] (B) Mossy fiber field EPSPs are measured before and after tetanic stimulation in the absence (○) or presence (●) of 10–20 mM of the nonselective ionotropic glutamate receptor antagonist kynurenate (n = 5 each). Kynurenate has no effect on mossy fiber LTP, even though it blocks the field EPSP. [Reprinted with permission from ref. 26 (Copyright 1994, Elsevier Science).] (C) Mossy fiber field EPSPs are measured before and after tetanization (arrows). The first tetanus is given in the presence of the GluR5-specific antagonist LY382884 and the NMDAR antagonist AP-5 and does not induce mossy fiber LTP. A second tetanus without LY382884, however, does induce mossy fiber LTP. [Reprinted with permission from ref. 33 (Copyright 1999, MacMillan Magazines, Ltd., www.nature.com).] (D) Mossy fiber EPSCs are recorded in slices from wild-type, GluR5-deficient, and GluR6-deficient mice. Tetanization at time = 0 induces robust mossy fiber LTP in wild-type and GluR5-deficient mice, but only weak mossy fiber LTP in GluR6-deficient mice. [Reprinted with permission from ref. 24 (Copyright 2001, Elsevier Science).]