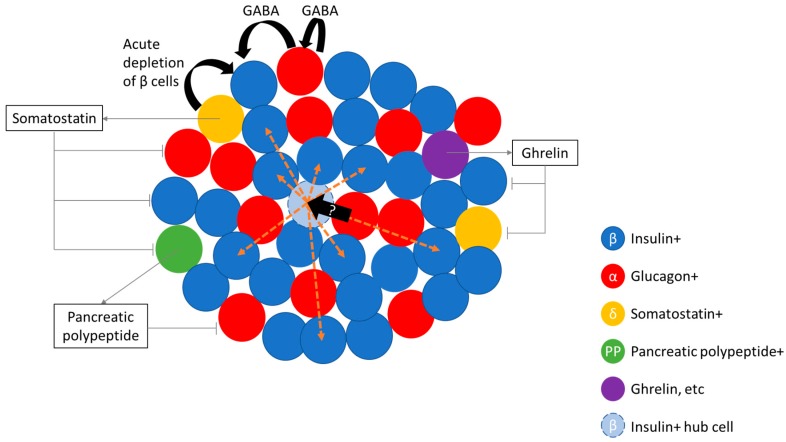
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram showing the interdependency of islet cells. Evidence in the literature points to the possibility of the transdifferentiation (solid black arrows) of α-cells (red circle) via stimulation by gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA), and δ-cells (yellow circle) into insulin-containing β (like)-cells (blue circle). It is currently unclear whether the replenishment of β-cells from the transdifferentiation of α-cells is able to replace hub β-cells (light blue circle) which influence (yellow arrows) the function of other β-cells. Somatostatin, released from δ-cells, can inhibit the release of glucagon, insulin, and pancreatic polypeptide from α-, β-, and PP cells (green circle), respectively. Pancreatic polypeptide, released from PP cells, can inhibit the release of glucagon. Ghrelin, released from ghrelin-positive islet cells (purple circle), can inhibit insulin and somatostatin secretion.