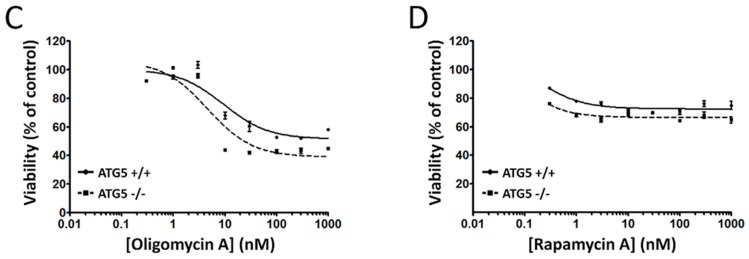
Figure 6.
Comparison of ATG5+/+ and ATG5−/− cell viability in response to known modulators of autophagy. Concentration-dependent changes in the viability of wild-type and ATG5-null mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) after exposure to (A) thapsigargin, (B) tunicamycin, (C) oligomycin A, and (D) rapamycin A. ATG5+/+ and ATG5−/− cells were exposed, in parallel, to increasing concentrations of each compound (0.3 nM to 1 µM) for 48 h. Cell viability was determined by a WST-8 proliferation/cytotoxicity assay, with the viability of vehicle-treated cells defined as 100%. Data points show mean viability ± SE (n = 3 wells per treatment) from a representative comparison that was repeated in three independent experiments.