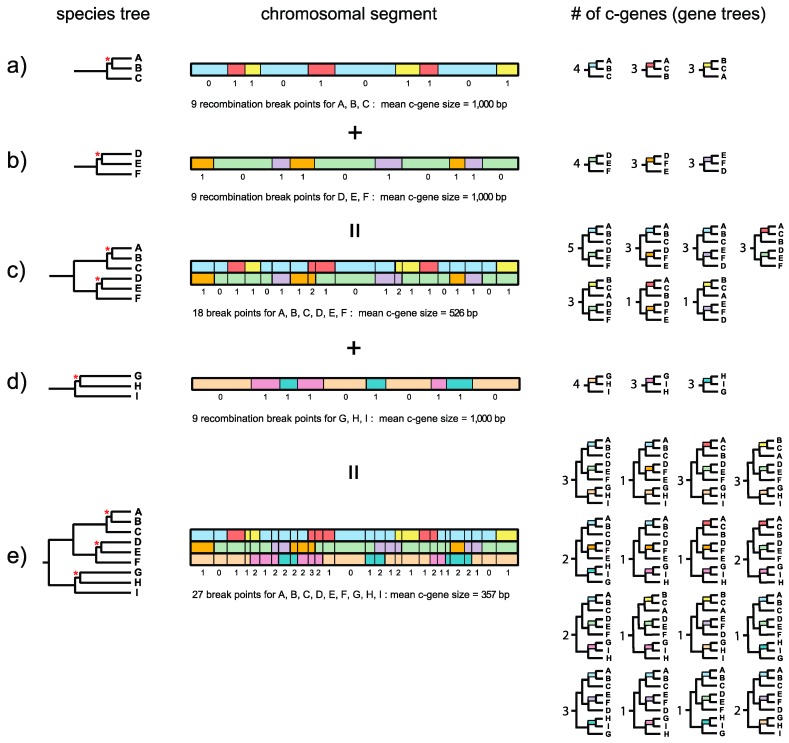
Figure 1.
Illustration of the recombination ratchet for a hypothetical 10-kb chromosomal segment of DNA and a phylogeny with nine taxa and three short internodes, each of which results in incomplete lineage sorting and deep coalescence for a local subtree with three taxa. The three short internodes (internal branches) are labeled with red asterisks. Other internal branches are longer, and deep coalescence does not occur. The three subtrees are for taxa A-B-C (a); D-E-F (b); and G-H-I (d). Incomplete lineage sorting for each set of three taxa (a,b,d) is associated with nine recombination breakpoints and ten c-genes of average length 1000 bp. For each set of three taxa there are three different genealogical histories with contrasting topological relationships (genealogical histories for the same topology but with different branch lengths are ignored). Numbers below c-genes correspond to Robinson–Foulds (RF) distances [24], sensu Sul and Williams [25], relative to the species tree. Note that for each chromosomal segment with only three taxa (panels a,b,d), the maximum RF distance is 1. The overlay of nine recombination breakpoints for A-B-C and nine recombination breakpoints for D-E-F results in a total of 18 recombination breakpoints and 19 c-genes for the six-taxon phylogeny (A-B-C-D-E-F) (panel c). Average c-gene size for the 10-kb chromosomal segment with six-taxa is 526 bp. Nine different topologies are possible for these six taxa, of which seven are represented among the 19 c-genes. The maximum RF distance is 2 for c-genes based on six taxa (panel c). The overlay of 18 recombination breakpoints for A-B-C-D-E-F with nine recombination breakpoints for G-H-I results in 27 recombination breakpoints and 28 c-genes for the nine-taxon phylogeny (A-B-C-D-E-F-G-H-I) (panel e). For the nine-taxon phylogeny, mean c-gene size is reduced to 357 bp. Among the 28 c-genes for the nine-taxon phylogeny, 16 of 27 possible topologies are represented (panel e).