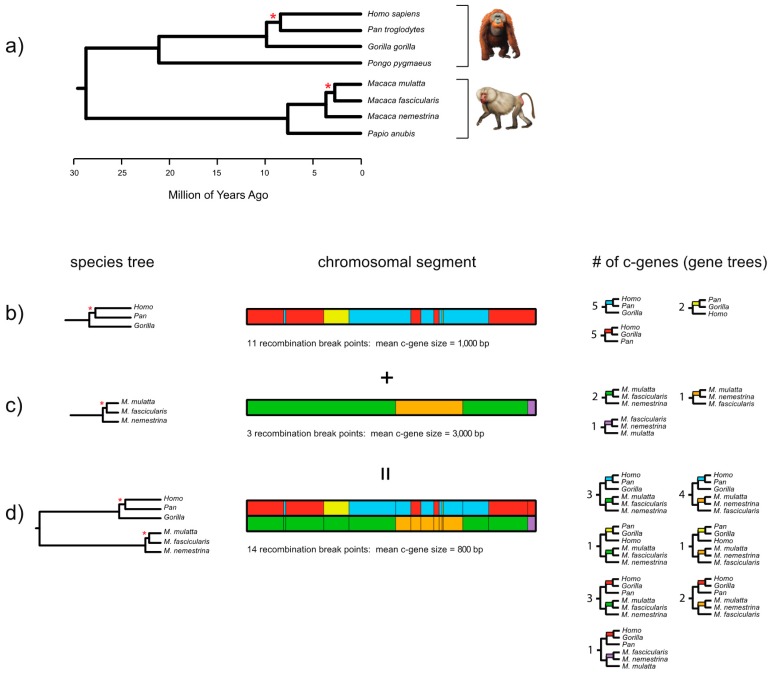
Figure 2.
Results of four-gamete test (FGT) for the ARMC3 gene (~120.1 kb alignment). The FGT was applied separately to two subtrees of primates (panel a)—four hominids (Homo, Pan, Gorilla, Pongo) and four cercopithecids (3 Macaca spp., Papio). Primate relationships are as in Springer et al. [71]. The FGT was applied to the entire ARMC3 gene from start codon to stop codon, but the results are only illustrated for the first 12 kb of the alignment. Recombination breakpoints and c-gene trees are shown for hominids (panel b) and Macaca spp. (panel c). In both cases there are three possible topologies, all of which are represented by one or more c-gene trees (the outgroups Pongo and Papio are not shown). Panel (d) shows the results of the recombination ratchet, where overlay of 11 recombination breakpoints for hominids and three recombination breakpoints for Macaca results in 14 recombination breakpoints and 15 c-genes for the 12 kb alignment (panel d). Among the nine topologies that are possible for the two subtrees of three taxa, seven are represented among the 15 c-gene trees (panel d). Paintings of Pongo and Papio by Carl Buell.