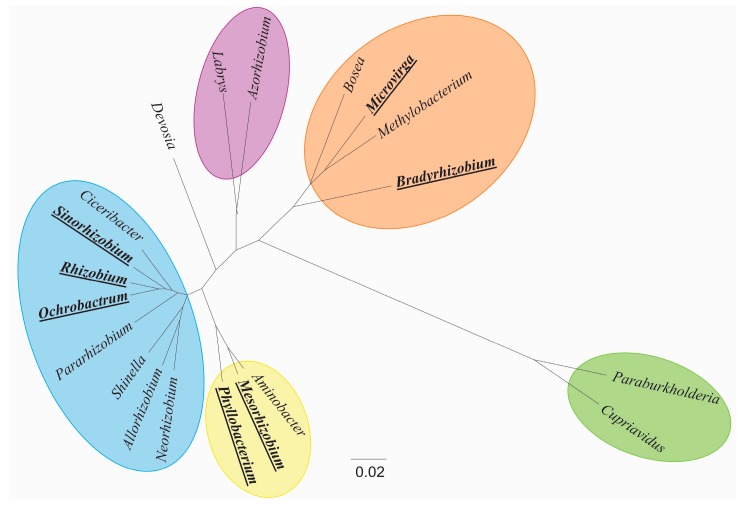
Figure 1.
A Bayesian posterior probability consensus tree based on 1408 bps of 16S rRNA derived from 16 rhizobial and 4 related genera (the genera nodulating Genisteae are in bold case-underlined). The strains used for this construction and the 16S rRNA Genbank accession numbers were: Rhizobium leguminosarum ATCC 10004 (U29386), Sinorhizobium fredii ATCC 35423 (X67231), Allorhizobium undicola ATCC 700741 (Y17047), Pararhizobium capsulatum ATCC 43294 (X73042), Neorhizobium galegae ATCC 43677 (D11343), Shinella zoogloeoides ATCC 19623 (AB238789), Ciceribacter lividus MSSRFBL1 (NR 135717), Mesorhizobium loti ATCC 700743 (X67229), Aminobacter anthyllidis STM 4645(FR869633), Phyllobacterium brassicacearum LMG 22836 (AY785319), Ochrobactrum lupini LMG 22726 (AY457038), Methylobacterium marchantiae DSM 21328 (FJ157976), Bradyrhizobium lupini USDA 3051 (KM114861), Bosea lupini LMG 26383 (FR774992), Azorhizobium oxalatiphilum DSM 18749 (FR799325), Labrys okinawensis DSM 18385 (AB236169), Devosia honganensis ACCC 19737 (KP339871), Paraburkholderia caribensis CCUG 42847 (Y17009), Cupriavidus alkaliphilus LMG 26294 (HQ438078), and Microvirga lupini LMG 26460 (EF191408). The 16S rRNA sequences were aligned in MUSCLE [16] and implemented in MEGA 6.0 [17]. The Bayesian analyses were performed using BEAST 1.7 software [18]. The model of nucleotide evolution used in all of the analyses was GTR + I + G, as selected by the jModel Test software [19]. The Yule process was selected as a tree prior to Bayesian analysis, 10,000,000 generations were performed and the tree was visualized and edited using FigTree version 1.3.1 software [20].