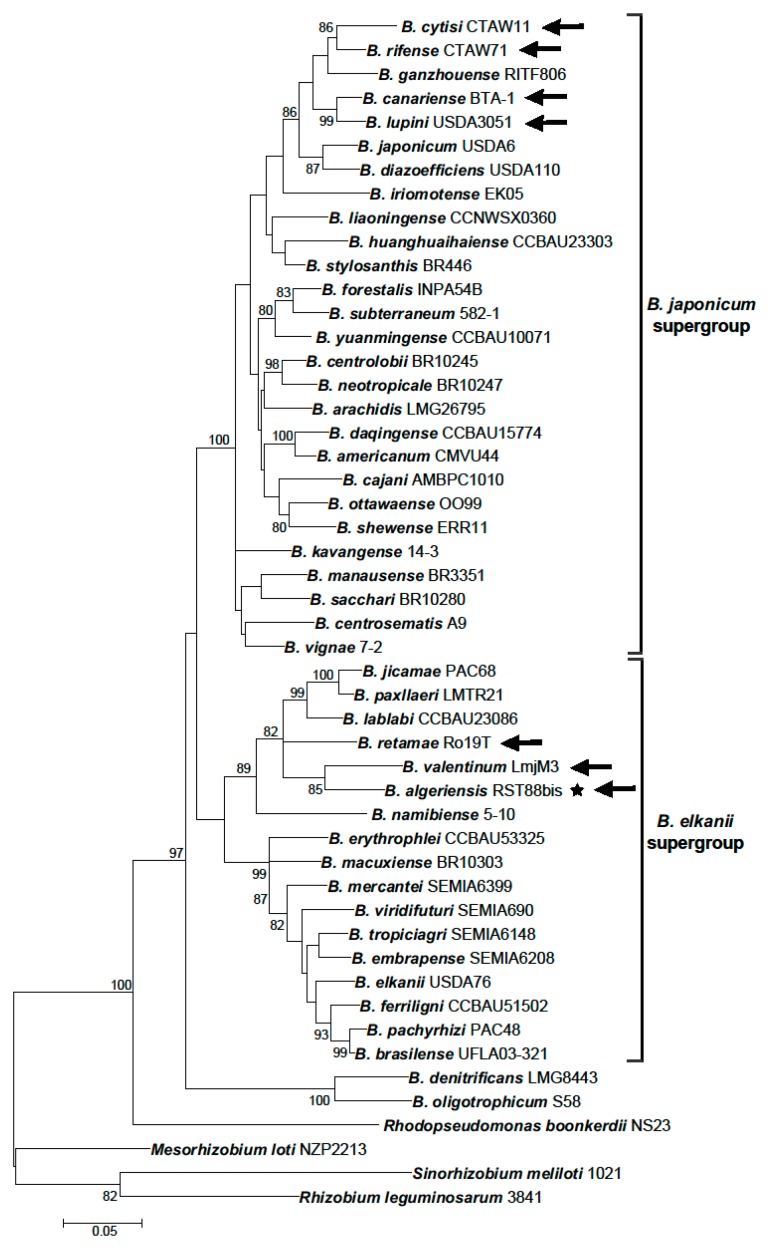
Figure 2.
Maximum likelihood (ML) phylogeny of concatenated recA and glnII partial gene sequences (425 bp + 519 bp), comprising type strains of Bradyrhizobium species with the exception of species, in which recA sequences were missing: Bradyrhizobium betae LMG 21987, Bradyrhizobium guangdongense CCBAU 51649, Bradyrhizobium guangxiense CCBAU 53363, Bradyrhizobium icense LMTR 13 and Bradyrhizobium ingae BR 10250. The scale bar indicates the number of substitutions per site. Bootstrap values >70% (percentage of 500 replicates calculated under distance criteria) are given at the branching nodes. The sequences of Rhodopseudomonas boonkerdii NS23, M. loti NZP2213, Sinorhizobium meliloti 1021 and R. leguminosarum 3841 were used as outgroups. The sequences were aligned using ClustalW software and ML phylogenies were inferred with Mega 6 [17] using the best-fit nucleotide substitution models as indicated by jModelTest 2.1.4. [115]. The distances were calculated according to the GTR+I+G model. Arrows indicate Bradyrhizobium species that nodulate Genisteae plants. Asterisk denotes Bradyrhizobium algeriensis, which has not been formally recognized.