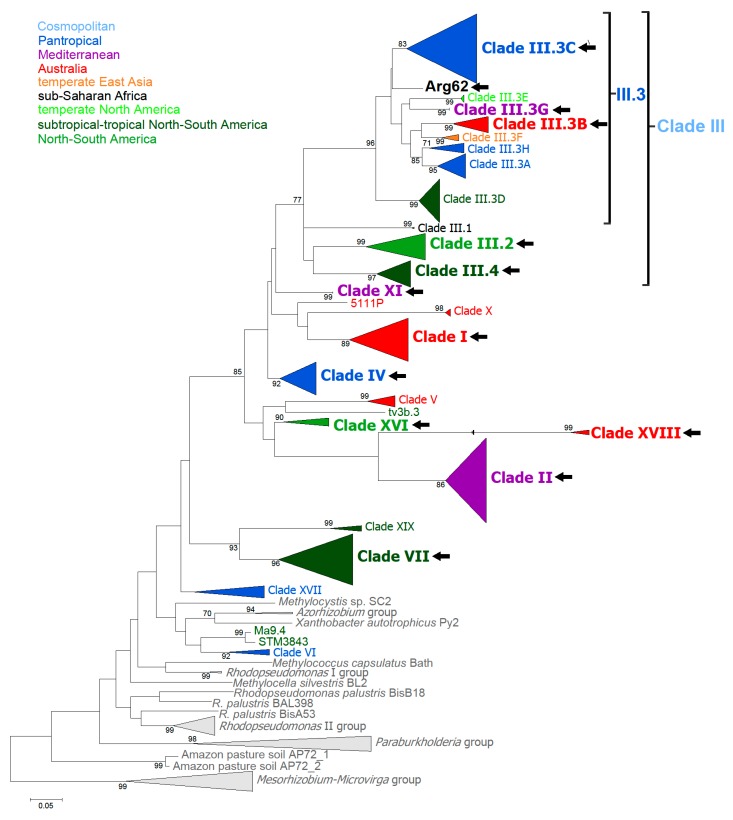
Figure 3.
Maximum likelihood (ML) tree based on bradyrhizobial nifD gene sequences (759 bp). The significance of each branch is indicated by the bootstrap percentage calculated for 500 bootstraps. The bootstrap values greater than 70% are indicated at nodes. The sequences were aligned using ClustalW software and ML phylogenies were inferred with Mega 6 [17] using the best-fit nucleotide substitution models, as indicated by jModelTest 2.1.4. [115]. The distances were calculated according to the HKY+I+G model. Because of the substitution saturation that is associated with the third codon position in the nifD dataset, as estimated using DAMBE 5 [133] these positions were excluded from further analysis. The number of sequences used in the construction of this phylogenetic tree is given in brackets: Bradyrhizobium: (640); Rhodopseudomonas (29); Paraburkholderia/Burkholderia (19); Mesorhizobium (22); Microvirga (3); Azorhizobium (2). The number of Bradyrhizobium sequences included in a particular clade or branch is also shown in brackets: Clade I (54), Clade II (106), Clade III(III.1) (2), Clade III(III.2) (33), Clade III(III.3A) (31), Clade III(III.3B) (22), Clade III(III.3C) (87), Clade III(III.3D) (54), Clade III(III.3E) (9), Clade III(III.3F) (8), Clade III(III.3G) (3), Clade III(III.3H) (12), Clade III(III.4) (33), Clade IV (41), Clade V (14), Clade VI (7), Clade VII (64), Clade X (9), Clade XI (2), Clade XVI (10), Clade XVIII (6), Clade XIX (7), Clade XX (15). Black arrows indicate Bradyrhizobium species nodulating Genisteae plants.